|
Option Name
|
Description
|
|
Methods
|
|
Confidence
level
|
specifies the significance
level to use for the construction of confidence intervals.
|
|
Statistics
|
|
You can choose to include
the default statistics in the results or choose to include additional
statistics.
|
|
Parameter Estimates
|
|
Standardized
regression coefficients
|
displays the standardized
regression coefficients. A standardized regression coefficient is
computed by dividing a parameter estimate by the ratio of the sample
standard deviation of the dependent variable to the sample standard
deviation of the regressor.
|
|
Confidence
limits for estimates
|
displays the 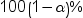 upper and lower confidence limits for the parameter
estimates.
|
|
Sums of Squares
|
|
Sequential
sum of squares (Type I)
|
displays the sequential
sums of squares (Type I SS) along with the parameter estimates for
each term in the model.
|
|
Partial
sum of squares (Type II)
|
displays the partial
sums of squares (Type II SS) along with the parameter estimates for
each term in the model.
|
|
Partial and Semipartial
Correlations
|
|
Squared
partial correlations
|
displays the squared
partial correlation coefficients computed by using Type I and Type
II sums of squares.
|
|
Squared
semipartial correlations
|
displays the squared
semipartial correlation coefficients computed by using Type I and
Type II sums of squares. This value is calculated as sum of squares
divided by the corrected total sum of squares.
|
|
Diagnostics
|
|
Analysis
of influence
|
requests a detailed
analysis of the influence of each observation on the estimates and
the predicted values.
|
|
Analysis
of residuals
|
requests an analysis
of the residuals. The results include the predicted values from the
input data and the estimated model, the standard errors of the mean
predicted and residual values, the studentized residual, and Cook’s D statistic
to measure the influence of each observation on the parameter estimates.
|
|
Predicted
values
|
calculates predicted
values from the input data and the estimated model.
|
|
Multiple Comparisons
|
|
Perform
multiple comparisons
|
specifies whether to
compute and compare the least squares means of fixed effects.
|
|
Select the
effects to test
|
specifies the effects
that you want to compare. You specified these effects on the Model tab.
|
|
Method
|
requests a multiple
comparison adjustment for the p-values and
confidence limits for the differences of the least squares means.
Here are the valid methods: Bonferroni, Nelson, Scheffé, Sidak,
and Tukey.
|
|
Significance
level
|
requests that a t type
confidence interval be constructed for each of the least squares means
with a confidence level of 1 – number. The value of number
must be between 0 and 1. The default value is 0.05.
|
|
Collinearity
|
|
Collinearity
analysis
|
requests a detailed
analysis of collinearity among the regressors. This includes eigenvalues,
condition indices, and decomposition of the variances of the estimates
with respect to each eigenvalue.
|
|
Tolerance
values for estimates
|
produces tolerance values
for the estimates. Tolerance for a variable is defined as 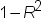 , where R square is obtained from the regression
of the variable on all other regressors in the model.
|
|
Variance
inflation factors
|
produces variance inflation
factors with the parameter estimates. Variance inflation is the reciprocal
of tolerance.
|
|
Heteroscedasticity
|
|
Heteroscedasticity
analysis
|
performs a test to confirm
that the first and second moments of the model are correctly specified.
|
|
Asymptotic
covariance matrix
|
displays the estimated
asymptotic covariance matrix of the estimates under the hypothesis
of heteroscedasticity and heteroscedasticity-consistent standard errors
of parameter estimates.
|
|
Plots
|
|
Diagnostic and Residual
Plots
|
|
By default, several
diagnostic plots are included in the results. You can also specify
whether to include plots of the residuals for each explanatory variable.
|
|
More Diagnostic Plots
|
|
Rstudent
statistic by predicted values
|
plots studentized residuals
by predicted values. If you select the Label extreme points option,
observations with studentized residuals that lie outside the band
between the reference lines 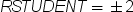 are deemed outliers.
|
|
DFFITS statistic
by observations
|
plots the DFFITS statistic
by observation number. If you select the Label extreme
points option, observations with a DFFITS statistic greater
in magnitude than 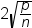 are deemed influential. The number of observations
used is n, and the number of regressors is p.
|
|
DFBETAS
statistic by observation number for each explanatory variable
|
produces panels of DFBETAS
by observation number for the regressors in the model. You can view
these plots as a panel or as individual plots. If you select the Label
extreme points option, observations with a DFBETAS statistic
greater in magnitude than 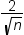 are deemed influential for that regressor. The number
of observations used is n.
|
|
Label extreme
points
|
identifies the extreme
values on each different type of plot.
|
|
Scatter Plots
|
|
Fit plot
for a single continuous variable
|
produces a scatter plot
of the data overlaid with the regression line, confidence band, and
prediction band for models with a single continuous variable. The
intercept is excluded. When the number of points exceeds the value
for the Maximum number of plot points option,
a heat map is displayed instead of a scatter plot.
|
|
Observed
values by predicted values
|
produces a scatter plot
of the observed values versus the predicted values.
|
|
Partial
regression plots for each explanatory variable
|
produces partial regression
plots for each regressor. If you display these plots in a panel, there
is a maximum of six regressors per panel.
|
|
Maximum
number of plot points
|
specifies the maximum
number of points to include in each plot.
|