Example: Analyzing Age and Gender
-
data pr; input Person Gender $ y1 y2 y3 y4; y=y1; Age=8; output; y=y2; Age=10; output; y=y3; Age=12; output; y=y4; Age=14; output; drop y1-y4; datalines; 1 F 21.0 20.0 21.5 23.0 2 F 21.0 21.5 24.0 25.5 3 F 20.5 24.0 24.5 26.0 4 F 23.5 24.5 25.0 26.5 5 F 21.5 23.0 22.5 23.5 6 F 20.0 21.0 21.0 22.5 7 F 21.5 22.5 23.0 25.0 8 F 23.0 23.0 23.5 24.0 9 F 20.0 21.0 22.0 21.5 10 F 16.5 19.0 19.0 19.5 11 F 24.5 25.0 28.0 28.0 12 M 26.0 25.0 29.0 31.0 13 M 21.5 22.5 23.0 26.5 14 M 23.0 22.5 24.0 27.5 15 M 25.5 27.5 26.5 27.0 16 M 20.0 23.5 22.5 26.0 17 M 24.5 25.5 27.0 28.5 18 M 22.0 22.0 24.5 26.5 19 M 24.0 21.5 24.5 25.5 20 M 23.0 20.5 31.0 26.0 21 M 27.5 28.0 31.0 31.5 22 M 23.0 23.0 23.5 25.0 23 M 21.5 23.5 24.0 28.0 24 M 17.0 24.5 26.0 29.5 25 M 22.5 25.5 25.5 26.0 26 M 23.0 24.5 26.0 30.0 27 M 22.0 21.5 23.5 25.0 ;
Click to create the Work.Pr data set.
to create the Work.Pr data set.
-
TipIf the data set is not available from the drop-down list, click
 . In the Choose a Table window,
expand the library that contains the data set that you want to use.
Select the data set for the example and click OK.
The selected data set should now appear in the drop-down list.
. In the Choose a Table window,
expand the library that contains the data set that you want to use.
Select the data set for the example and click OK.
The selected data set should now appear in the drop-down list.
-
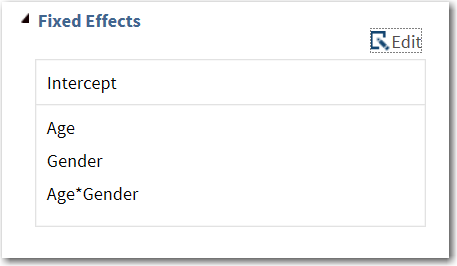
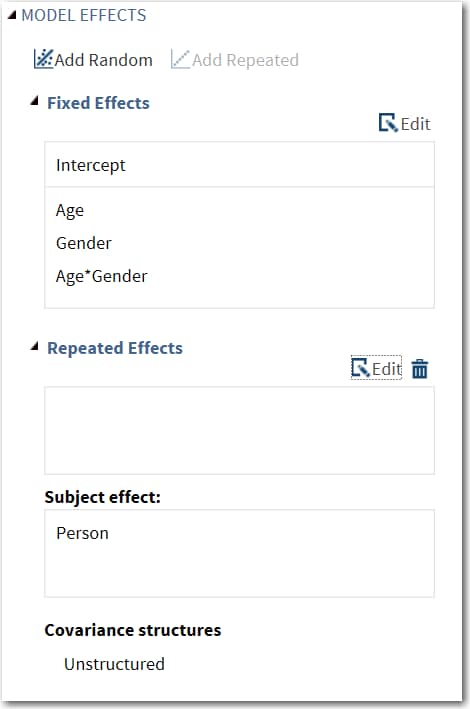
Here is the result on the Model tab:
-
On the Options tab:
-
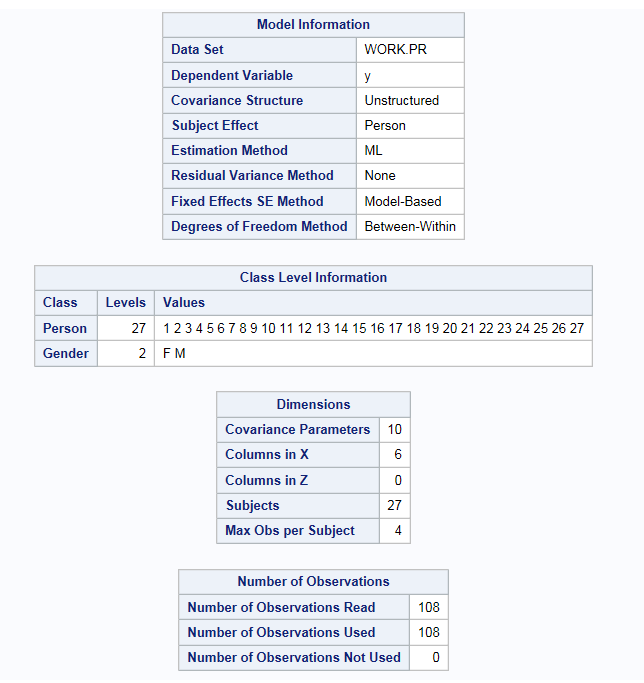
In the Estimated method drop-down list, select Maximum likelihood.
-
In the Select statistics to display drop-down list, select Default and additional statistics.
-
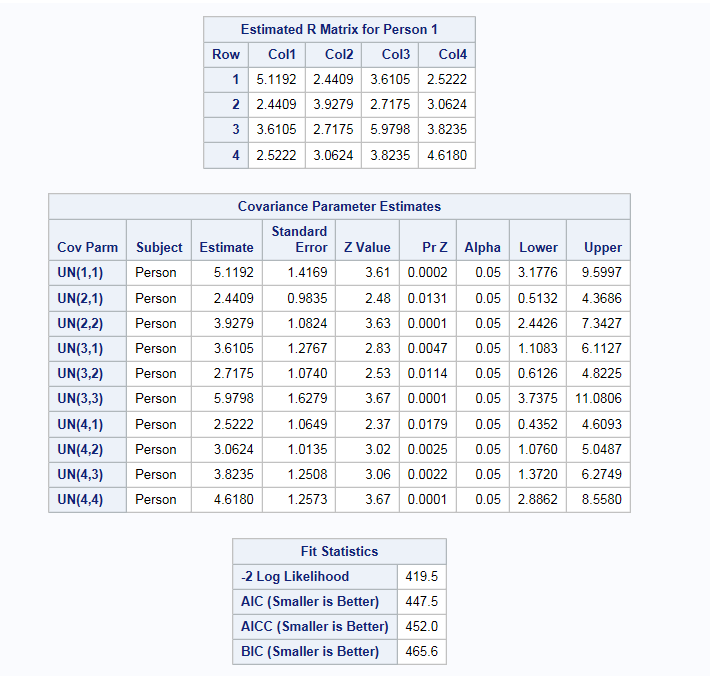
Expand the Tests heading, and select Standard errors and Wald Test of covariance parameters.
-
Expand the Parameter Estimates heading. Under the Fixed Effects heading, select Show parameter estimates. Under the Repeated Effect heading, select Estimated R matrix.
-
-
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.