VSAM Data Access Types
Sequential Access
Direct Access
Introduction to Direct Access
With direct access, data storage or retrieval depends
only on the location of the record and not on a reference to records
previously accessed. Each record is stored or retrieved directly, according to its logical address (its key
or its relative-record number, or RRN), or its address relative to
the beginning of the data set (relative-byte address, or RBA). Thus,
there are two direct access modes: keyed by key or relative-record number, and addressed by relative-byte address.
Keyed Direct Access
Addressed Direct Access
In addressed direct access, the entire data set is treated
as a continuous stream of bytes. A record is retrieved and stored
directly by its address relative to the beginning of the data set
(relative-byte address, or RBA), which is dependent on the record's
location relative to records previously accessed. SAS supports addressed
access to logical records in ESDS and KSDS data sets. It also supports
addressed access (read-only) to control intervals in all three data
set types.
Keyed Direct Access with an Alternate Index
An alternate key index, commonly
called an alternate index (AIX), provides another way to access a
VSAM data set. The advantage of an alternate index is that you effectively
reorganize the data set instead of keeping separate copies organized
in different ways for different applications. Suppose you have a KSDS
with the employee number as the prime key. By building alternate indexes
using employee names and department numbers, you can access the same
data set in three ways: by employee name, by employee number, or by
department number. The alternate key does not have to be unique. That
is, there can be more than one record with the same alternate key.
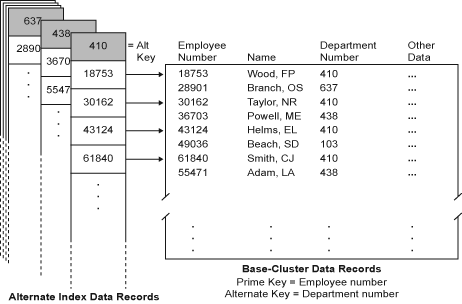
The following figure
illustrates an alternate index with nonunique keys over a KSDS. The
base cluster records are sequenced by employee number, which is the
prime key. The alternate index records are sequenced by department
number, which is the alternate key. Each alternate index data record
points to the prime key (employee number) in the base cluster. Note
that because the alternate keys are nonunique, there can be multiple
base records with the same department number.
Alternate indexes can be built over a KSDS or an ESDS.
You define and build an alternate index using the IBM utility program
Access Method Services (AMS). The data set over which an alternate
index is built is called the base cluster. The alternate key can be
any field having a fixed length and a fixed position within each record.
The alternate index itself is a KSDS. The data component of an alternate
index contains the alternate key, followed by a pointer to the appropriate
record or records in the base cluster. In a KSDS, the pointer is the
prime key; in an ESDS, the pointer is the RBA of the base record or
records.
A path logically relates
a base cluster and one of its alternate indexes. You define and name
a path to access the base cluster records through a specific alternate
index with AMS. Using Alternate Indexes for VSAM Data SetsSee and IBM Documentation for more information about defining alternate indexes.
Skip Sequential Access
A combination of both direct and sequential
access can be used in a two-step process called skip sequential access.
The process uses keyed direct access to find a starting point. After
the initial record is obtained, additional records are retrieved sequentially.
Skip sequential processing can be used with a KSDS, RRDS, and, if
it has an alternate index, an ESDS.