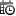Using Data Items in a Query
About Data Items
Each data source includes
one or more standard data items. You decide which data items to use
to define a query for a report section. You can use all the data items
in the data source or a subset of data items. Each data item is classified
as either a category or a measure.
Category 

A data item whose distinct
values are used to group and aggregate measures. There are four types
of categories: alphanumeric, date, timestamp, and time. Alphanumeric
categories can be made up of all letters, all digits, or a combination
of the two. Categories that have values that are all digits might
be physically stored as character or numeric data. The data type affects
how values are handled in relation to some functionality, such as
filtering, sorting, and formatting.
Select Data Items
To select data items
to use in the query for the current report section: