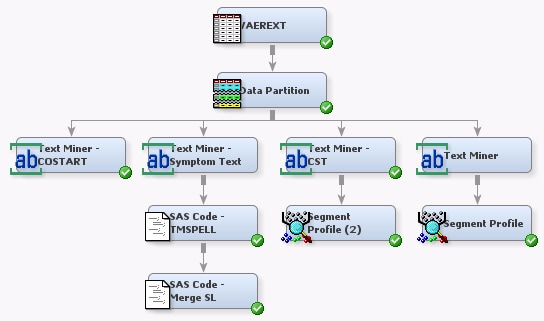
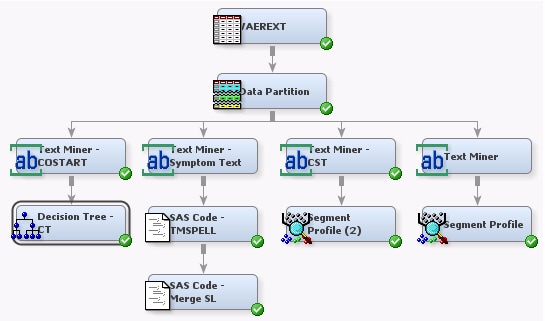
To use the COSTRING variable
to create a model:
-
Select
the
Text Mining tab on the toolbar and drag
and drop a Text Miner node into the diagram workspace. Connect the
Data Partition node to the Text Miner node.
-
Right-click
the new Text Miner node and select
Rename. Type
Text Miner — COSTART in the Node Name box, and click
OK.
-
Select
the VAEREXT node in the diagram workspace. Click the
button for the
Variables property in the Properties panel for the VAEREXT node.
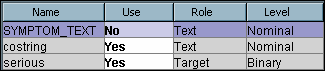
Recall
that there were two text variables, COSTRING and SYMPTOM_TEXT, from
the initial data source. By default, SAS Text Miner will use the longer
text variable, SYMPTOM_TEXT. In this chapter, you want to mine the
COSTRING variable.
Click
OK to close the Variables window.
-
Select
the Text Miner — COSTART node. Set the following properties
in the Properties panel for the Text Miner — COSTART node:
-
Click the

button for the
Variables property. In the Variables window, set the
Use value for the
SYMPTOM_TEXT variable to
No, the
Use value for the
costring variable to
Yes, and
the
Use value for the
serious variable to
Yes. Click
OK to save your changes.
-
Click the

button to the right of the
Stop List property. Select the
No data set to be specified check box in the Select a SAS Table dialog box. This removes the
entry for the stop list so that no stop list is used. Click
OK.
-
Set
Different Parts
of Speech to
No.
-
Right-click
the Text Miner — COSTART node, and select
Run. Click
Yes in the Confirmation dialog box.
Click
OK in the Run Status dialog box when
the node has finished running.
-
In the
Properties panel, make sure that the
Parse Variable property of the Text Miner — COSTART Terms node is set to
costring.
-
Click
the

button for the
Interactive property to open the Interactive Results window. One problem with
COSTART is that it does not always use the same keyword to describe
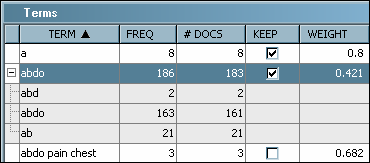
the same term or equivalent terms. For example,
abdomen is shown in COSTART as
ab and as
abdo. Sometimes there are modifiers that you do not
need. You could run the TMSPELL procedure, but because these are abbreviations,
the procedure probably will not find all of the correct spellings.
You need to manually clean some terms.
-
Sort the
terms in the Terms window by clicking on the Term column heading.
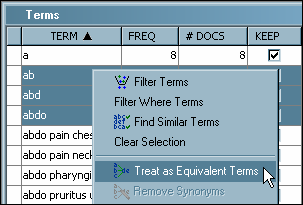
Select
ab,
abd,
and
abdo from the TERM column. Right-click
and select
Treat as Equivalent Terms.
Select
abdo from the Create Equivalent Terms dialog box. Click
OK.
Look through
the data set and create synonyms by holding the CTRL or Shift keys
and clicking the terms that you consider to be the same. Then, right-click
on these selected terms and select
Treat as Equivalent
Terms.
-
Repeat
this process as many times as you need. It might be helpful to filter
the terms so that you can view the full text of COSTART before combining
terms.
-
Select
File  Save Synonyms
Save Synonyms from the Interactive Results window menu. Select
Mylib in the drop-down menu for the library field, and
type
COSTARTSYNS in the Data
Set Name field. Click
OK.
-
Close
the Text Miner — Interactive window.
-
Note that
the
Synonyms property in the Properties panel
has been set to the new MYLIB.COSTARTSYNS synonym data set.
-
COSTART
terms should represent keywords, so you want to create variables for
each keyword. Set the following
Transform properties in the Properties panel:
-
-
Set
Term Weight to
Mutual Information.
-
Set
Roll up Terms to
Yes.
-
Set
No. of Rolled-up
terms to
400.
-
Set
Drop Other Terms to
Yes.
-
Right-click
the Text Miner — COSTART node, and select
Run. Click
Yes in the Confirmation dialog box.
Click
OK in the Run Status dialog box when
the node has finished running.
-
Click
the

button for the Interactive property to open the Text
Miner — Interactive window and view the Terms window.
-
Sort the
TERM column until the arrow on the column heading is pointing up.
Note: Terms with
a plus (+) sign indicate the synonyms that you have specified. Click
the plus (+) sign to expand the child terms underneath the respective
parent term.
-
Scroll
down until you see terms that do not have a checkmark beneath the
Keep column. A separate variable will not be created for these terms.
They were not considered significant enough (based on rolling up only
400 variables) to create a separate variable. Recall that you set
the
Roll up Terms property to
Yes and the
No. of Rolled-up Terms property to
400. When you roll up terms,
the terms are sorted in descending order of the value of the term
weight times the square root of the number of documents. The top 400
highest-ranked terms are then used as variables in the document collection.
-
Close
the Text Miner — Interactive window.
-
From the
Model tab, drag and drop a Decision Tree node into the
diagram workspace. Connect the Text Miner — COSTART node to
the Decision Tree node. Right-click the Decision Tree node, and select
Rename. Type
Decision Tree —
CT, where “CT” stands for “COSTART
Terms.” Click
OK.
-
Right-click
the Decision Tree — CT node and select
Run. Click
Yes in the Confirmation dialog box.
Recall that when you created the VAEREXT data set, you set
serious as the target variable.
-
Click
Results in the Run Status dialog box after the node
has finished running.
-
Select
View  Assessment
Assessment 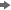 Classification Chart: serious
Classification Chart: serious from the Results window menu to view the Classification Chart.
Note: Blue indicates
correct classification, and red indicates incorrect classification.
-
Close
the Results window.
 button for the Variables property in the Properties panel for the VAEREXT node.
button for the Variables property in the Properties panel for the VAEREXT node.
 button for the Interactive property to open the Interactive Results window. One problem with
COSTART is that it does not always use the same keyword to describe
the same term or equivalent terms. For example, abdomen is shown in COSTART as ab and as abdo. Sometimes there are modifiers that you do not
need. You could run the TMSPELL procedure, but because these are abbreviations,
the procedure probably will not find all of the correct spellings.
You need to manually clean some terms.
button for the Interactive property to open the Interactive Results window. One problem with
COSTART is that it does not always use the same keyword to describe
the same term or equivalent terms. For example, abdomen is shown in COSTART as ab and as abdo. Sometimes there are modifiers that you do not
need. You could run the TMSPELL procedure, but because these are abbreviations,
the procedure probably will not find all of the correct spellings.
You need to manually clean some terms.