Overview of Writing a Stored Process
A stored process is a SAS program that is hosted on
a server and described by metadata. Stored processes can be written
by anyone who is familiar with the SAS programming language or with
the aid of a SAS code generator such as SAS Enterprise Guide. The
basic steps for creating a stored process are as follows:
-
Choose or define a server. For more information, see Choosing or Defining a Server.
-
Register the stored process metadata. For more information, see Registering the Stored Process Metadata.
Almost any SAS program
can be a stored process. A stored process can be written using the
SAS program editor, SAS Enterprise Guide, or any text editor. The
following program is a typical stored process:
%STPBEGIN;
title 'Age analysis by sex';
footnote;
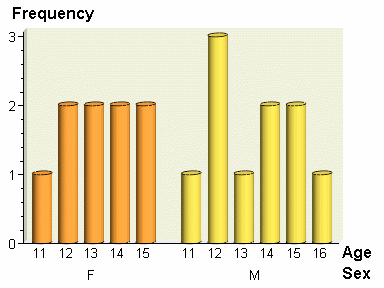
proc sort data=sashelp.class out=class; by sex age; run;
proc gchart data=class;
vbar3d age / group=sex
discrete
nozero
shape=cylinder
patternid=group;
run; quit;
title;
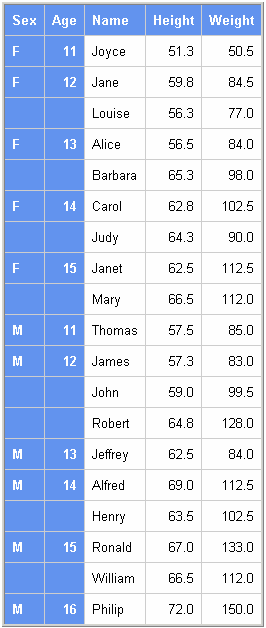
proc print data=class;
by sex age;
id sex age;
var name height weight;
run;
%STPEND;The %STPBEGIN and %STPEND macros initialize the Output Delivery System (ODS) and deliver
the output to the client. This stored process is capable of generating
multiple output formats, including HTML, XML, PDF, CSV, and custom
tagsets and then delivering the output through packages or streaming
output. For more
information, see Setting Result Capabilities.
Note: Because the %STPBEGIN and
%STPEND macros initialize the Output Delivery System (ODS), you should
use them only if your stored process creates ODS output. They are
not necessary if the stored process is creating only a table and does
not create a report. Another case where they should not be used is
when your stored process writes directly to the _WEBOUT fileref, either
using the DATA step or some other method. Writing to _WEBOUT is a
common technique used in SAS/IntrNet programs.