Shared Concepts and Topics
References
-
Afifi, A. A., and Azen, S. P. (1972). Statistical Analysis: A Computer-Oriented Approach. New York: Academic Press.
-
Beale, E. M. L. (1972). “A Derivation of Conjugate Gradients.” In Numerical Methods for Nonlinear Optimization, edited by F. A. Lootsma, 39–43. London: Academic Press.
-
Browne, M. W. (1982). “Covariance Structures.” In Topics in Applied Multivariate Analysis, edited by D. M. Hawkins, 72–141. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
-
Dennis, J. E., Gay, D. M., and Welsch, R. E. (1981). “An Adaptive Nonlinear Least-Squares Algorithm.” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 7:348–368.
-
Dennis, J. E., and Mei, H. H. W. (1979). “Two New Unconstrained Optimization Algorithms Which Use Function and Gradient Values.” Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications 28:453–482.
-
Dunnett, C. W. (1980). “Pairwise Multiple Comparisons in the Unequal Variance Case.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 75:796–800.
-
Edwards, D., and Berry, J. J. (1987). “The Efficiency of Simulation-Based Multiple Comparisons.” Biometrics 43:913–928.
-
Eskow, E., and Schnabel, R. B. (1991). “Algorithm 695: Software for a New Modified Cholesky Factorization.” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 17:306–312.
-
Fletcher, R. (1987). Practical Methods of Optimization. 2nd ed. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Fox, J. (1987). “Effect Displays for Generalized Linear Models.” In Sociological Methodology, edited by C. C. Clogg, 347–361. Washington, DC: American Sociological Association.
-
Frankel, S. A. (1961). “Statistical Design of Experiments for Process Development of MBT.” Rubber Age 89:453.
-
Friendly, M. (2000). Visualizing Categorical Data. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc.
-
Games, P. A., and Howell, J. F. (1976). “Pairwise Multiple Comparison Procedures with Unequal n’s and/or Variances: A Monte Carlo Study.” Journal of Educational Statistics 1:113–125.
-
Gay, D. M. (1983). “Subroutines for Unconstrained Minimization.” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 9:503–524.
-
Guirguis, G. H., and Tobias, R. D. (2004). “On the Computation of the Distribution for the Analysis of Means.” Communications in Statistics—Simulation and Computation 33:861–888.
-
Hastie, T. J., Tibshirani, R. J., and Friedman, J. H. (2001). The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction. New York: Springer-Verlag.
-
Holm, S. (1979). “A Simple Sequentially Rejective Multiple Test Procedure.” Scandinavian Journal of Statistics 6:65–70.
-
Hsu, J. C. (1992). “The Factor Analytic Approach to Simultaneous Inference in the General Linear Model.” Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics 1:151–168.
-
Hsu, J. C. (1996). Multiple Comparisons: Theory and Methods. London: Chapman & Hall.
-
Hsu, J. C., and Peruggia, M. (1994). “Graphical Representation of Tukey’s Multiple Comparison Method.” Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics 3:143–161.
-
Kenward, M. G., and Roger, J. H. (1997). “Small Sample Inference for Fixed Effects from Restricted Maximum Likelihood.” Biometrics 53:983–997.
-
Kramer, C. Y. (1956). “Extension of Multiple Range Tests to Group Means with Unequal Numbers of Replications.” Biometrics 12:307–310.
-
Kutner, M. H. (1974). “Hypothesis Testing in Linear Models (Eisenhart Model).” American Statistician 28:98–100.
-
Moré, J. J. (1978). “The Levenberg-Marquardt Algorithm: Implementation and Theory.” In Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol. 30, edited by G. A. Watson, 105–116. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
-
Moré, J. J., and Sorensen, D. C. (1983). “Computing a Trust-Region Step.” SIAM Journal on Scientific and Statistical Computing 4:553–572.
-
Myers, R. H. (1976). Response Surface Methodology. Blacksburg: Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University.
-
Nelson, P. R. (1982). “Exact Critical Points for the Analysis of Means.” Communications in Statistics—Theory and Methods 11:699–709.
-
Nelson, P. R. (1991). “Numerical Evaluation of Multivariate Normal Integrals with Correlations
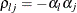 .” In Frontiers of Statistical Scientific Theory and Industrial Applications: Proceedings of the ICOSCO I Conference, edited by A. Öztürk, and E. C. van der Meulen, 97–114. Columbus, OH: American Sciences Press.
.” In Frontiers of Statistical Scientific Theory and Industrial Applications: Proceedings of the ICOSCO I Conference, edited by A. Öztürk, and E. C. van der Meulen, 97–114. Columbus, OH: American Sciences Press.
-
Nelson, P. R. (1993). “Additional Uses for the Analysis of Means and Extended Tables of Critical Values.” Technometrics 35:61–71.
-
Ott, E. R. (1967). “Analysis of Means: A Graphical Procedure.” Industrial Quality Control 24:101–109. Reprinted in Journal of Quality Technology 15 (1983): 10–18.
-
Polak, E. (1971). Computational Methods in Optimization. New York: Academic Press.
-
Powell, M. J. D. (1977). “Restart Procedures for the Conjugate Gradient Method.” Mathematical Programming 12:241–254.
-
Powell, M. J. D. (1978a). “Algorithms for Nonlinear Constraints That Use Lagrangian Functions.” Mathematical Programming 14:224–248.
-
Powell, M. J. D. (1978b). “A Fast Algorithm for Nonlinearly Constrained Optimization Calculations.” In Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol. 630, edited by G. A. Watson, 144–175. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
-
Powell, M. J. D. (1982a). “Extensions to Subroutine VF02AD.” In Systems Modeling and Optimization, Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences, vol. 38, edited by R. F. Drenick, and F. Kozin, 529–538. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
-
Powell, M. J. D. (1982b). VMCWD: A Fortran Subroutine for Constrained Optimization. Technical Report DAMTP 1982/NA4, Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge.
-
Royen, T. (1989). “Generalized Maximum Range Tests for Pairwise Comparisons of Several Populations.” Biometrical Journal 31:905–929.
-
Shaffer, J. P. (1986). “Modified Sequentially Rejective Multiple Test Procedures.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 81:826–831.
-
Silvapulle, M. J., and Sen, P. K. (2004). Constrained Statistical Inference: Order, Inequality, and Shape Constraints. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Tamhane, A. C. (1979). “A Comparison of Procedures for Multiple Comparisons of Means with Unequal Variances.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 74:471–480.
-
Westfall, P. H. (1997). “Multiple Testing of General Contrasts Using Logical Constraints and Correlations.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 92:299–306.
-
Westfall, P. H., Tobias, R. D., Rom, D., Wolfinger, R. D., and Hochberg, Y. (1999). Multiple Comparisons and Multiple Tests Using the SAS System. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc.
-
Westfall, P. H., and Young, S. S. (1993). Resampling-Based Multiple Testing: Examples and Methods for p-Value Adjustment. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Winer, B. J. (1971). Statistical Principles in Experimental Design. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill.