| The TRANSREG Procedure |
| Model Statement Usage |
Here are some examples of model statements:
model identity(y) = identity(x);
a linear model with a nonlinear regression function
model identity(y) = spline(x / nknots=5);
model identity(y) = identity(x1-x5);
multiple regression with nonlinear transformations
model spline(y / nknots=3) = spline(x1-x5 / nknots=3);
multiple regression with nonlinear but monotone transformations
model mspline(y / nknots=3) = mspline(x1-x5 / nknots=3);
multivariate multiple regression
model identity(y1-y4) = identity(x1-x5);
model identity(y1-y4) = identity(x1-x5) / method=canals;
model identity(y1-y4) = identity(x1-x5) / method=redundancy;
preference mapping, vector model (Carroll; 1972)
model identity(Attrib1-Attrib3) = identity(Dim1-Dim2);
preference mapping, ideal point model (Carroll; 1972)
model identity(Attrib1-Attrib3) = point(Dim1-Dim2);
preference mapping, ideal point model, elliptical (Carroll; 1972)
model identity(Attrib1-Attrib3) = epoint(Dim1-Dim2);
preference mapping, ideal point model, quadratic (Carroll; 1972)
model identity(Attrib1-Attrib3) = qpoint(Dim1-Dim2);
model identity(Subj1-Subj50) = class(a b c d e f / zero=sum);
model monotone(Subj1-Subj50) = class(a b c d e f / zero=sum);
main effects, two-way interaction
model identity(y) = class(a|b);
less-than-full-rank model—main effects and two-way interaction are constrained to sum to zero
model identity(y) = class(a|b / zero=sum);
main effects and all two-way interactions
model identity(y) = class(a|b|c@2);
main effects and all two- and three-way interactions
model identity(y) = class(a|b|c);
main effects and only the b*c two-way interaction
model identity(y) = class(a b c b*c);
seven main effects, three two-way interactions
model identity(y) = class(a b c d e f g a*b a*c a*d);
deviations-from-means (effects or
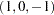 ) coding, with an a reference level of ’1’ and a b reference level of ’2’
) coding, with an a reference level of ’1’ and a b reference level of ’2’ model identity(y) = class(a|b / deviations zero='1' '2');
cell-means coding (implicit intercept)
model identity(y) = class(a*b / zero=none);
model identity(y) = class(a|b / zero='1' '1');
reference line with change in line parameters
model identity(y) = class(a) | identity(x);
reference curve with change in curve parameters
model identity(y) = class(a) | spline(x);
separate curves and intercepts
model identity(y) = class(a / zero=none) | spline(x);
quantitative effects with interaction
model identity(y) = identity(x1 | x2);
separate quantitative effects with interaction within each cell
model identity(y) = class(a * b / zero=none) | identity(x1 | x2);
Copyright © 2009 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.