| The POWER Procedure |
Analyses in the TWOSAMPLESURVIVAL Statement
Rank Tests for Two Survival Curves (TEST=LOGRANK, TEST=GEHAN, TEST=TARONEWARE)
The method is from Lakatos (1988) and Cantor (1997, pp. 83–92).
Define the following notation:
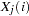 |
 |
|||
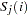 |
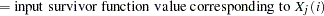 |
|||
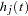 |
 |
|||
 |
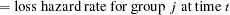 |
|||
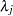 |
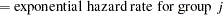 |
|||
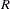 |
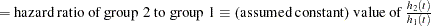 |
|||
 |
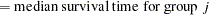 |
|||
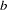 |
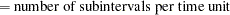 |
|||
 |
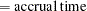 |
|||
 |
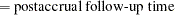 |
|||
 |
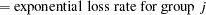 |
|||
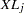 |
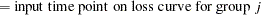 |
|||
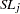 |
 |
|||
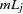 |
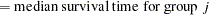 |
|||
 |
 |
Each survival curve can be specified in one of several ways.
For exponential curves:
a single point
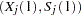 on the curve
on the curve median survival time
hazard rate
hazard ratio (for curve 2, with respect to curve 1)
For piecewise linear curves with proportional hazards:
a set of points
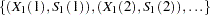 (for curve 1)
(for curve 1) hazard ratio (for curve 2, with respect to curve 1)
For arbitrary piecewise linear curves:
a set of points
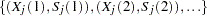
A total of 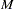 evenly spaced time points
evenly spaced time points 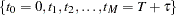 are used in calculations, where
are used in calculations, where
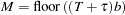 |
The hazard function is calculated for each survival curve at each time point. For an exponential curve, the (constant) hazard is given by one of the following, depending on the input parameterization:
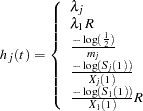 |
For a piecewise linear curve, define the following additional notation:
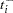 |
 |
|||
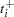 |
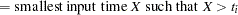 |
The hazard is computed by using linear interpolation as follows:
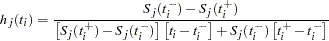 |
With proportional hazards, the hazard rate of group 2’s curve in terms of the hazard rate of group 1’s curve is
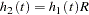 |
Hazard function values  for the loss curves are computed in an analogous way from
for the loss curves are computed in an analogous way from 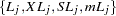 .
.
The expected number at risk 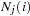 at time
at time  in group
in group 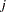 is calculated for each group and time points
is calculated for each group and time points 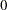 through
through 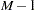 , as follows:
, as follows:
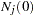 |
 |
|||
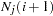 |
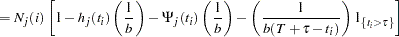 |
Define 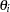 as the ratio of hazards and
as the ratio of hazards and 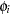 as the ratio of expected numbers at risk for time
as the ratio of expected numbers at risk for time  :
:
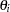 |
 |
|||
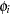 |
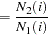 |
The expected number of deaths in each subinterval is calculated as follows:
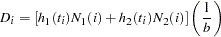 |
The rank values are calculated as follows according to which test statistic is used:
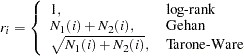 |
The distribution of the test statistic is approximated by  where
where
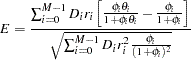 |
Note that  can be factored out of the mean
can be factored out of the mean 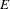 , and so it can be expressed equivalently as
, and so it can be expressed equivalently as
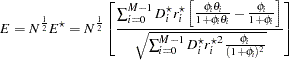 |
where 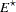 is free of
is free of 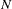 and
and
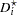 |
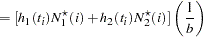 |
|||
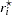 |
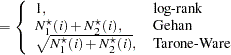 |
|||
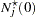 |
 |
|||
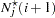 |
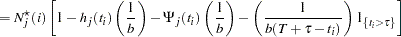 |
The approximate power is
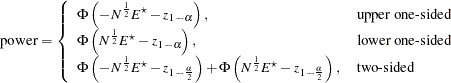 |
Note that the upper and lower one-sided cases are expressed differently than in other analyses. This is because 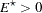 corresponds to a higher survival curve in group 1 and thus, by the convention used in PROC power for two-group analyses, the lower side.
corresponds to a higher survival curve in group 1 and thus, by the convention used in PROC power for two-group analyses, the lower side.
For the one-sided cases, a closed-form inversion of the power equation yield an approximate total sample size
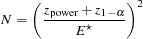 |
For the two-sided case, the solution for 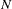 is obtained by numerically inverting the power equation.
is obtained by numerically inverting the power equation.
Copyright © 2009 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.