| The MDS Procedure |
| Formulas |
The following notation is used:
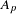
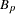
slope for partition p
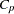
power for partition p
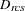
distance computed from the model between objects r and c for subject s
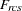
data weight for objects r and c for subject s obtained from the cth WEIGHT variable, or 1 if there is no WEIGHT statement
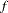
value of the FIT= option
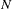
number of objects
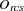
observed dissimilarity between objects r and c for subject s
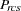
partition index for objects r and c for subject s
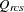
dissimilarity after applying any applicable estimated transformation for objects r and c for subject s
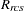
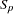
standardization factor for partition p
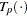
estimated transformation for partition p
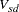
coefficient for subject s on dimension d
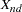
coordinate for object n on dimension d
Summations are taken over nonmissing values.
Distances are computed from the model as
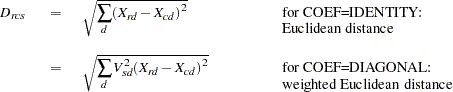 |
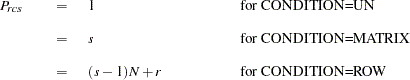 |
The estimated transformation for each partition is
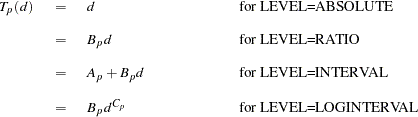 |
For LEVEL=ORDINAL, 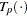 is computed as a least-squares monotone transformation.
is computed as a least-squares monotone transformation.
For LEVEL=ABSOLUTE, RATIO, or INTERVAL, the residuals are computed as
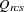 |
 |
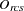 |
|||
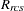 |
 |
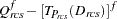 |
For LEVEL=ORDINAL, the residuals are computed as
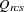 |
 |
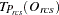 |
|||
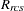 |
 |
 |
If 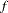 is 0, then natural logarithms are used in place of the
is 0, then natural logarithms are used in place of the 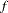 th powers.
th powers.
For each partition, let
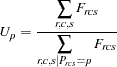 |
and
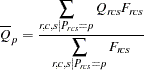 |
Then the standardization factor for each partition is
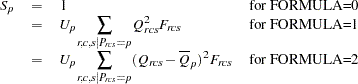 |
The badness-of-fit criterion that the MDS procedure tries to minimize is
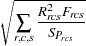 |
Copyright © 2009 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.