The SPD Server Client/Server Model
Overview of the Client/Server Model
SPD Server software
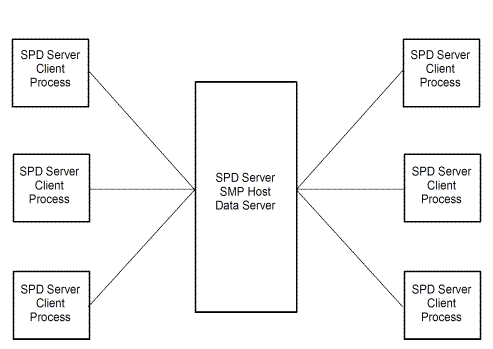
divides SAS processing loads between the client and server. The following
diagram shows a simple client/server topology. The server hosts multiple
concurrent clients while it performs the heaviest processing tasks.
Typical clients are desktop PCs or low-end UNIX workstations that
are running front-end software. The front-end application sends the
client's data requests over the network to the server and processes
the information that the server returns.
You can create one or
more SPD Servers on the host server machine. When an SPD Server host
receives a client's data request, it performs an action on behalf
of the client. The action depends on the request that was received.
Where does the user
fit into the SPD Server client/server model? Users initiate SPD Server
client sessions. In this documentation, the term user refers
to the operator of an SPD Server client.
SPD Server Host Services for Clients
SPD Server hosts provide
multiple services to SPD Server clients:
-
Reduces network traffic SPD Server reads, sorts, and subsets entire SAS tables, and then returns answer sets. A query subset replaces large file downloads to the client machine. SPD Server uses a common storage facility. Multiple client users can use the same SAS data on the server without each client having to transfer the SAS data to their workstations.
|
SPD Server Feature
|
SPD Server
Client Action
|
SPD Server
Host Response
|
|---|---|---|
|
Support for petabytes
of data
|
The SPD Server client
reads existing SAS tables with a PROC COPY statement, or creates an
SPD Server table by using a SAS DATA step or procedure. SPD Server
clients can also use SQL pass-through CREATE, COPY, or LOAD statements
to read SAS tables.
|
The SPD Server host
creates component files that consist of one or more physical partition
files. The server stores the physical partition files in one or more
device or directory paths.
|
|
Scalable SMP Support
|
The SPD Server client
runs SAS procedures and SQL pass-through syntax to read, sort, index,
or query an SPD Server table.
|
The SPD Server host
uses its threaded operating system to perform concurrent processing
tasks that are distributed across multiple processors.
|
|
Selective Parallel Queries
|
The SPD Server client
uses WHERE clause or SQL SELECT syntax. SQL pass-through, PROC SQL,
and WHERE alternatives that are not part of SAS are supported.
|
The SPD Server host
supports and subsets SPD Server tables, and then delivers answer sets
to clients.
|
|
Parallel Loads
|
The SPD Server client
runs SAS procedures by using the LOAD or COPY command to store SAS
data and indexes.
|
The SPD Server host
uses multiple threads to load and store tables and indexes.
|
|
Parallel Indexes
|
The SPD Server client
creates table indexes using a DATA step, the DATASETS procedure with
an INDEX option, or SQL pass-through with the LOAD or COPY command.
|
The SPD Server host
creates SPD Server table indexes in parallel.
|
|
SAS Data Security
|
The SPD Server client
accesses the SPD Server host using SQL pass-through, a LIBNAME statement,
or an alternative connection that is not part of SAS.
|
The SPD Server host
secures SPD Server files at the LIBNAME domain level, the table level,
or both, and the row level.
|
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.