Dynamic Cluster Table Operations
Creating Dynamic Cluster Tables
To create dynamic cluster
tables in SPD Server, you must have a set of related SPD Server tables
that you want to cluster, such as tables that contain monthly sales
transactions. The SPD Server tables that you want to cluster must
all be in the same domain. They must use identical table structures
(columns and indexes) and compression. However, member table partition
sizes and member table owners can vary. These requirements ensure
the metadata compatibility that is necessary to create dynamic cluster
tables in SPD Server.
After you have organized
the SPD Server tables, issue a PROC SPDO command to bind the tables
into a dynamic cluster table.
Syntax
The general form for
the PROC SPDO cluster create command is:
CLUSTER CREATE cluster-tablenameMEM|MEMBER=membername
<MAXSLOT=max-slot-num-spec><UNIQUEINDEX=YES|NO>
<DELETE=YES|NO> ;
Arguments
cluster-tablename
the name of the cluster
table to be created
member name
the member table name
<max-slot-num-spec>
the maximum number
of slots, or member tables, to be allocated for the dynamic cluster.
The default SPD Server setting for the MAXSLOT= parameter is -1. This
value configures SPD Server to permit dynamic growth of the number
of member tables in a cluster up to the specified system maximum value.
The system maximum value for the number of slots is specified by the
MAXGENNUM variable setting in the spdsserv.parm configuration file.
If there is a known maximum number of slots to be enforced for a particular
dynamic cluster table, it is more efficient to specify the limitation
using the MAXSLOT= parameter when issuing the PROC SPDO CREATE CLUSTER
command.
Options
UNIQUEINDEX=YES|NO
validates a unique
index. The default setting is
YES.
DELETE=YES|NO
permanently deletes
the cluster and its members. The default setting is
NO.
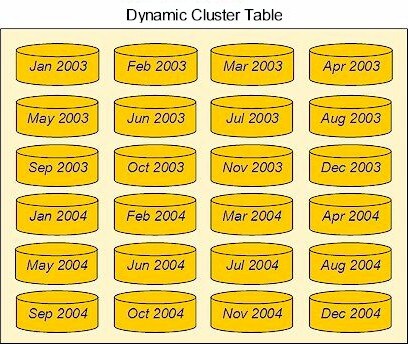
Dynamic Cluster Table shows a dynamic
cluster table with 24 members. Each member table is an SPD Server
table that contains monthly sales transactions.
The following code shows
the PROC SPDO command syntax that creates the dynamic cluster table
from the member tables:
PROC SPDO library=domain-name;
cluster create Sales_History
mem=sales200301
mem=sales200302
mem=sales200303
mem=sales200304
mem=sales200305
mem=sales200306
mem=sales200307
mem=sales200308
mem=sales200309
mem=sales200310
mem=sales200311
mem=sales200312
mem=sales200401
mem=sales200402
mem=sales200403
mem=sales200404
mem=sales200405
mem=sales200406
mem=sales200407
mem=sales200408
mem=sales200409
mem=sales200410
mem=sales200411
mem=sales200412
quit ;
PROC SPDO uses a LIBRARY
statement to identify the domain that contains the tables to be clustered.
The CLUSTER CREATE syntax specifies the name of the dynamic cluster
table to be created (Sales_History).
MEM= identifies the
members of the dynamic cluster table. The tables in the example represent
monthly sales transactions. This example uses 24 monthly sales tables
for the years 2003 and 2004.
Dynamic Cluster Table Examples contains more extensive code examples of creating dynamic
cluster tables.
Verify Dynamic Cluster Table Control Access
You must have SPD Server
Control access to any member tables that you use in the CLUSTER CREATE
or CLUSTER ADD commands. You must also have SPD Server Control access
to the dynamic cluster table itself to submit a CLUSTER UNDO command.
There is no restriction on table ownership if you have Control access
to all the member tables. All users that have access to a domain have
default Control access to tables that were created by the user Anonymous
within that domain. Access control lists (ACLs) can be defined on
a dynamic cluster table after it is created. The permissions that
are specified in the dynamic cluster table ACL are applied when SPD
Server accesses the dynamic cluster table. Any individual ACL that
is defined on a member table does not apply during the time when the
member table is part of a created dynamic cluster table.
Add Tables to a Dynamic Cluster Table
To add tables to a dynamic
cluster table, you must have an existing dynamic cluster table. The
SPD Server tables that you want to add to the dynamic cluster table
must all be in the same domain as the dynamic cluster table. They
must use identical table structures (columns and indexes) and compression.
However, member table partition sizes and member table owners can
vary. These requirements ensure the metadata compatibility that is
required to add to a dynamic cluster table.
After the SPD Server
tables are organized, issue a PROC SPDO command to add the tables
to an existing dynamic cluster table.
The general form of
the PROC SPDO CLUSTER ADD command is as follows:
Syntax
CLUSTER ADD cluster-tablename MEM|MEMBER=membername ;
Arguments
cluster-tablename
the name of the cluster
table to be created
membername
the member table name.
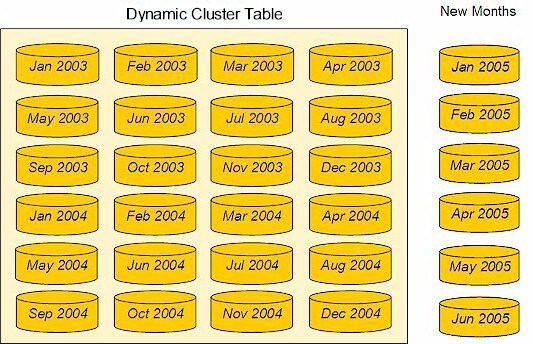
New Monthly Data to Add to an Existing Dynamic Cluster Table shows
sales tables for the first six months of 2005. These tables are set
up to be added to the dynamic cluster table that contains monthly
sales transactions data for 2003 and 2004, which was reviewed in
Creating Dynamic Cluster Tables.
The following code shows
the PROC SPDO command syntax that adds the new tables to an existing
dynamic cluster table:
PROC SPDO library=domain-name;
cluster add Sales_History
mem=sales200501
mem=sales200502
mem=sales200503
mem=sales200504
mem=sales200505
mem=sales200506;
quit;
PROC SPDO uses a LIBRARY
statement to identify the domain that contains the existing dynamic
cluster table that you want to add to. The CLUSTER ADD syntax specifies
the name of the dynamic cluster table that you want to add to (Sales_History).
MEM= identifies the
member tables of the table to be added to the existing dynamic cluster
table.
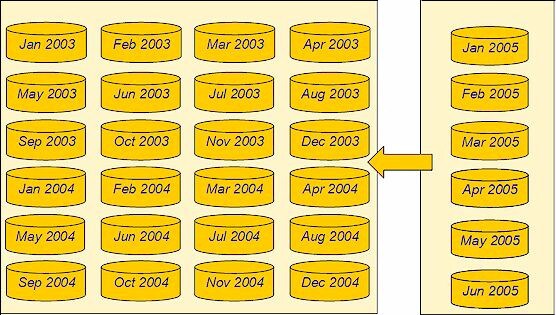
In
Adding Member Tables to a Dynamic Cluster Table, six tables
that include monthly sales transactions for the first half of 2005
are set up to be added to the existing dynamic cluster table that
contains 2003 and 2004 sales transactions data.
Dynamic Cluster Table Examples contains more extensive code examples of adding to a dynamic
cluster table.
Undo Dynamic Cluster Tables
To undo a dynamic cluster
table, you must have an existing dynamic cluster table. Undoing the
dynamic cluster table reverts the table back to its unbound SPD Server
tables.
The general form of
the PROC SPDO CLUSTER UNDO command is as follows:
Syntax
CLUSTER UNDO cluster-tablename ;
Arguments
cluster-tablename
the name of the cluster
table to undo.
Example
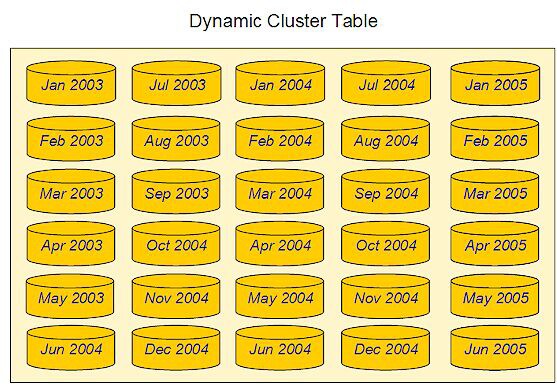
Dynamic Cluster Table with 30 Members shows a dynamic
cluster table with 30 members. Each member contains monthly sales
transactions for the years 2003 and 2004, and part of 2005.
The following code shows
the PROC SPDO command syntax to use to undo the dynamic cluster table
shown in
Dynamic Cluster Table with 30 Members:
PROC SPDO library=domain-name; cluster undo Sales_History; quit;
PROC SPDO uses a LIBRARY
statement to identify the domain that contains the existing dynamic
cluster table that you want to undo. The CLUSTER UNDO syntax specifies
the name of the dynamic cluster table that you want to undo (Sales_History).
Unbound Dynamic Cluster Table
shows the dynamic cluster table unbound.
Dynamic Cluster Table Examples contains more extensive code examples of undoing a dynamic
cluster table.
Refreshing Dynamic Cluster Tables
Overview of Refreshing Dynamic Cluster Tables
Over time, member tables
in a dynamic cluster table can age out. When this occurs, the member
tables in dynamic cluster need to be refreshed, or replaced with more
current and updated tables. An example of refreshing an SPD Server
dynamic cluster is updating a dynamic cluster table every month. The
dynamic cluster table's members are tables that contain the previous
24 months of sales transactions data.
To refresh dynamic cluster
table contents in SPD Server, use the PROC SPDO CLUSTER UNDO command
to unbind the cluster. Next, you make the member table changes to
update the cluster. Then you re-bind the dynamic cluster table using
the PROC SPDO CREATE CLUSTER command.
SPD Server 5.2 features
options that enable you to refresh dynamic cluster tables without
unbinding and re-binding the cluster. The process of using CLUSTER
UNDO and CREATE CLUSTER to refresh tables causes the dynamic cluster
table to be temporarily unavailable. The SPD Server 5.2 dynamic cluster
table refresh methods CLUSTER REMOVE / ADD, and CLUSTER REPLACE,
do not require for the clusters to be unbound and reformed, and as
such, have no out-of-service latency requirements .
What are the differences
between the CLUSTER REMOVE / ADD and CLUSTER REPLACE commands?
First, the CLUSTER REMOVE
/ ADD command set enables you to specify replacement parameters for
multiple cluster member tables in a single command, but the CLUSTER
REPLACE command replaces only one member table in the dynamic cluster.
Second, CLUSTER REMOVE
/ ADD and CLUSTER REPLACE also handle table slotting differently.
Table slotting refers to the physical table positioning and ordering
within the dynamic cluster member table matrix. The CLUSTER REPLACE
command only addresses single member tables, and a new member table
inserted using CLUSTER REPLACE will occupy the same slot as the replaced
table. The CLUSTER REMOVE / ADD command removes tables from their
original slots, but appends the added tables to the end of the cluster
member table list, in the order in which they were submitted in the
command syntax.
Refreshing Dynamic Cluster Tables with CLUSTER UNDO and CLUSTER CREATE
To refresh a dynamic
cluster table using CLUSTER UNDO and CLUSTER CREATE, you unbind the
dynamic cluster table using PROC SPDO CLUSTER UNDO, make the member
table changes, and then you use CLUSTER CREATE to re-bind the dynamic
cluster table.
Here is an illustration
of using the classical CLUSTER UNDO and CLUSTER CREATE commands to
refresh a dynamic cluster table:
Refreshed Dynamic Cluster Table shows the result
of undoing the cluster table shown in
Dynamic Cluster Table with 30 Members, and then refreshing
the dynamic cluster table that contains sales transaction tables for
the first six months of 2005.
Dynamic Cluster Table Examples contains a more extensive code example of unbinding a dynamic
cluster table and refreshing it by re-creating it with different member
tables.
Refreshing Dynamic Cluster Tables with CLUSTER REMOVE and CLUSTER ADD
The SPD Server PROC
SPDO CLUSTER REMOVE and CLUSTER ADD commands enable you to refresh
dynamic cluster tables without unbinding and re-binding the cluster,
and without making the dynamic cluster table temporarily unavailable
during refactoring.
The CLUSTER REMOVE /
ADD command set enables you to specify replacement member tables for
one or more member tables in a dynamic cluster that have aged out
or are otherwise not wanted. The CLUSTER REMOVE / ADD command removes
old member tables from their original position in the cluster member
table list, and appends new updated tables to the end of the cluster
member table list, in the order in which they were submitted in the
command syntax.
The PROC SPDO CLUSTER
REMOVE command removes one or more member tables from a dynamic cluster.
When a cluster member table is removed, users that currently have
that particular cluster open for Read access will not see the change,
until a subsequent open or reopen of the cluster is performed by the
user, after the remove command has completed. The same is true for
the CLUSTER ADD command: changes are not reflected until the cluster
is opened or reopened after the CLUSTER ADD processing is complete.
A cluster member table
that has been removed from a cluster becomes visible as a simple SPD
Server table, but the table remains in a read-only state. If there
is a need to update a member table that has been removed from a cluster,
use the CLUSTER FIX
MEMBER
Restoring Deleted Cluster Table Members command
to restore the member table to a writable state.
The general form of
the PROC SPDO CLUSTER REMOVE command is as follows:
Syntax
CLUSTER REMOVE cluster-tablename MEM= membername_1 MEM= membername_2 . . . MEM= membername_n ;
Arguments
cluster-tablename
the name of the dynamic
cluster to be edited.
membername_n
the name of one or
more member tables to be removed from the cluster.
Similarly, the general
form of the PROC SPDO CLUSTER ADD command is as follows:
Syntax
CLUSTER ADD cluster-tablename MEM= spd-tablename MEM= spd-tablename . . . MEM= spd-tablename ;
Arguments
cluster-tablename
the name of the dynamic
cluster to be edited.
spd-tablename
the name of one or
more member tables to be added to the cluster.
Refreshing Dynamic Cluster Tables with CLUSTER REPLACE
Like the CLUSTER REMOVE
and CLUSTER ADD command set, the SPD Server PROC SPDO CLUSTER REPLACE
command enables you to refresh dynamic cluster tables without unbinding
and re-binding the cluster.
The CLUSTER REPLACE
command enables you to specify a replacement member table for a single
member table in a dynamic cluster that has aged out or is otherwise
not wanted. The CLUSTER REPLACE command removes the old member table
from its original position in the cluster member table list, and replaces
the old member table with the new member table in the same slot (or
cluster position).
The PROC SPDO CLUSTER
REPLACE command replaces one member table from a dynamic cluster.
When a cluster member table is removed, users that currently have
that particular cluster open for Read access will not see the change,
until a subsequent open or reopen of the cluster is performed by the
user, after the replace command has completed.
A cluster member table
that has been replaced in a cluster becomes visible as a simple SPD
Server table, but the table remains in a read-only state. If there
is a need to update a member table that has been replaced from a cluster,
use the CLUSTER FIX
MEMBER
Restoring Deleted Cluster Table Members command
to restore the member table to a writable state.
The general form of
the CLUSTER REPLACE command is as follows:
Syntax
CLUSTER REPLACE cluster-tablename OLDMEMBER|OLDMEM= old-member-name NEWMEMBER|NEWMEM= new-member-name ;
Arguments
cluster-tablename
the name of the cluster
table in which you want to replace members.
old-member-name
the name of the old
member table that you want to remove from the cluster table.
new-member-name
the name of the new
member table that you want to insert into the cluster table.
Modify Dynamic Cluster Tables
PROC SPDO uses a CLUSTER
MODIFY command to modify a dynamic cluster table.
The general form for
the PROC SPDO CLUSTER MODIFY command is as follows:
Syntax
CLUSTER MODIFY cluster-tablename MINMAXVARLIST=(var1 var2 var3 ... var_n)
;
Arguments
cluster-tablename
the name of the cluster
table to be created.
var1
the name of the first
minmax variable to be added.
var_n
the name of the nth
minmax variable to be added.
Description
The CLUSTER MODIFY command
sets the MINMAXVARLIST attribute on variables that belong to an existing
dynamic cluster. The variable names that you specify on the CLUSTER
MODIFY command must exist in the dynamic cluster tables. The variables
must not have a preexisting MINMAXVARLIST setting. When the SPD Server
runs the CLUSTER MODIFY command, it unclusters the dynamic cluster
table and makes the variable modifications to the individual member
tables. The dynamic cluster table is re-created after the variable
modifications have completed. You must have Control access and Exclusive
access to the dynamic cluster table in order to run the CLUSTER MODIFY
command. SPD Server performs a full table scan to initialize the MINMAXVARLIST
values in each member table. As a result, the processor time required
for the CLUSTER MODIFY command is directly related to the sizes of
the tables that belong to the dynamic cluster table. If an error occurs
while the CLUSTER MODIFY command is running, the dynamic cluster table
cannot be re-created, and you need to manually re-create it by issuing
the CLUSTER CREATE command.
Create Dynamic Clusters with Unique Indexes
Use the UNIQUEINDEX
option on the CLUSTER CREATE command in PROC SPDO to specify whether
the unique indexes that are defined in the member tables should be
validated and marked as unique in the dynamic cluster table. If you
set the UNIQUEINDEX option to NO, then unique indexes are not validated,
and the dynamic cluster table metadata does not mark the indexes as
unique within the cluster. If you do not specify the UNIQUEINDEX option,
then the default setting YES is used. In this case, the indexes are
validated and marked as unique within the cluster. The processing
that is required to validate the unique indexes depends on the number
of rows in the tables. Processing can take considerable time for larger
tables. If you choose to use the validation process but the indexes
are not unique, the CLUSTER CREATE command fails.
CLUSTER CREATE clustername MEM=member_table_1 MEM=member_table_2 ... MEM=member_table_n UNIQUEINDEX=<yes|no>;
Destroy Dynamic Cluster Tables
You use the PROC SPDO
CLUSTER DESTROY command when you want to delete or destroy an existing
cluster table. The general form of the PROC SPDO CLUSTER DESTROY command
is as follows:
Syntax
CLUSTER DESTROY cluster-tablename ;
Arguments
cluster-tablename
the name of the cluster
table that you want to destroy.
The CLUSTER DESTROY
command is valid only when used on clusters that were created with
the DELETE=YES option configured.
Restoring Deleted Cluster Table Members
You use the PROC SPDO
CLUSTER FIX command when you need to restore removed or replaced cluster
member tables to a writable state. The general form for the PROC SPDO
CLUSTER FIX command is as follows:
Syntax
CLUSTER FIX member-tablename ;
Arguments
member-tablename
the name of the member
table that you want to repair.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.