Managing Large SPD Server Files
Managing large files is not only a performance issue;
it also has implications for file storage and disk space. Optimally,
an SPD Server administrator manages storage space for SPD Server LIBNAME
domains. In that case, you do not need to consider storage issues.
SPD Server does the work for you. Optimizing SAS Scalable Performance Data Server (SPD) Server contains more information about managing large SPD Server
files.
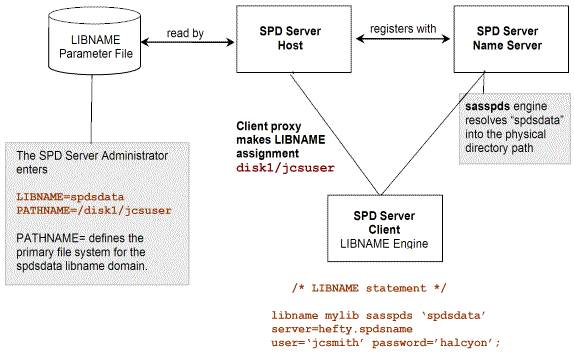
Initial Setup of SPD Server LIBNAME Domain Storage
The figure below shows
how an SPD Server domain is set up. An SPD Server administrator must
define the name and primary path for the domain in the LIBNAME parameter
file for SPD Server. The path that the administrator defines for each
domain is referred to as the primary file system for that domain.
SPD Server reads the LIBNAME parameter file at start-up. The SPD Server
registers the domains with the SPD Server name server. When the user
issues a LIBNAME statement, the client sends a message to the SPD
Server name server that resolves the domain name to its physical directory
path, and the client determines the SPD Server that registered the
domain.
Effect of the Administrator Option ROPTIONS=
After an SPD Server
administrator defines a primary file system for a domain, the administrator
can use LIBNAME parameter file options, identical to the DATAPATH=,
METAPATH=, and INDEXPATH= options in the LIBNAME statement, to set
up additional paths for the domain. However, the administrator can
restrict a user from defining additional paths using the LIBNAME statement
with the ROPTIONS= LIBNAME parameter file option. When an SPD Server
administrator uses the ROPTIONS= option, the administrator's
specification takes precedence over the user's specification. For more information,
see Configuring LIBNAME Domain Disk Space in SAS Scalable Performance Data Server: Administrator's Guide.
For example, assume
that a user uses the DATAPATH= option to specify a path to store table
data for a domain. If the SPD Server administrator also uses the DATAPATH=
option with ROPTIONS= for that domain entry in the LIBNAME parameter
file, the user's DATAPATH= specifications are ignored.
When the administrator
uses ROPTIONS= with path options, users are relieved of the complicated
task of managing disk space. Moreover, path information does not need
to be embedded in SAS programs. Instead, SAS jobs refer to only the
logical LIBNAME and rely on ROPTIONS= embedded by the administrator
to specify all of the physical path information. This approach uses
the power of the name server and lets it resolve path information
for an SPD Server domain.
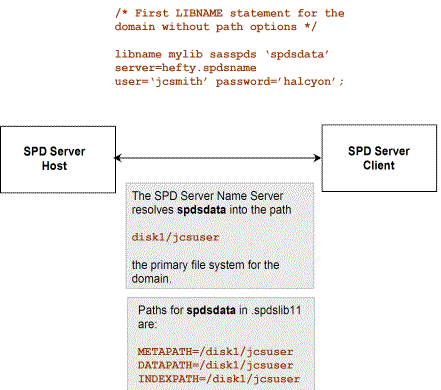
Using Explicit or Default Storage Paths
The first LIBNAME assignment
or SQL pass-through CONNECT statement that names a domain establishes
an initial set of paths for the domain. You can explicitly specify
the paths and manage your own disk space, or the software can establish
a default set of paths. The best choice is to use the default paths.
The following figure shows primary file system default paths:
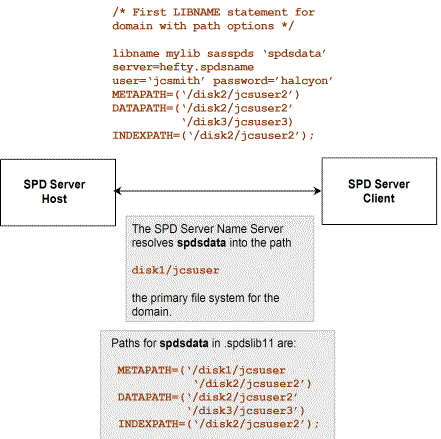
Explicit Initial Set of Paths shows an explicit initial set of paths.
The path options METAPATH=,
DATAPATH=, and INDEXPATH= store partitions for the components—metadata,
data, and indexes. Subsequent LIBNAME assignments augment the path
list that was created by the initial LIBNAME assignment. SPD Server
appends each new path assignment to any existing list for the component
file.
Unless you or an SPD
Server administrator specifies an initial set of paths, the software
uses the domain's primary file system in the LIBNAME parameter
file for the default path set. In the next section, information about
whether the default path set is ample for large tables or provides
optimal performance is discussed.
SPD Server Component Storage
SPD Server creates a
list of paths to be used for storing table files in an SPD Server
domain. If an SPD Server administrator did not use the ROPTIONS=
option,you can use path options to control file partition storage.
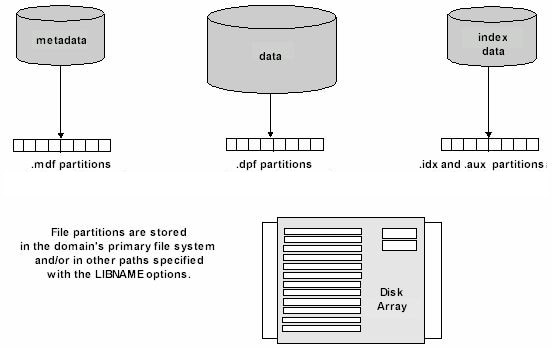
Each table consists
of a metadata component and a data component. Each component file
consists of one or more partition files on disk. The software requires
that the first metadata partition reside in the primary file system.
The primary file system is the path defined for the domain by an SPD
Server administrator. Other metadata partitions can overflow to additional
paths specified using the METAPATH= option.
If no paths are specified
for index and data components by the INDEXPATH= or DATAPATH= options,
SPD Server also stores these partitions in the primary file system.
If other paths are specified, it stores the initial partition for
these components in the first path that has available space. (Unlike
metadata partitions, data and index partitions do not have to start
in the primary file system.) A partition can expand until the path
is full. Remaining partitions overflow to the next path that has available
space, and so on.
Forced Partitioning of the Data Component
To improve parallel
processing of operations that involve full-table scans (for example,
WHERE clause evaluations without indexes or SQL GROUP BY evaluations),
you can force the creation of data component partitions at fixed-size
intervals. To specify the size interval, use the PARTSIZE= table option.
By default, the SPD Server sets PARTSIZE= to 16 MB. For more information,
see SAS Scalable Performance Data (SPD) Server Table Options
The SPD Server uses
the file systems that you specify with the DATAPATH= option to distribute
partitions in a cyclic, round-robin pattern. Instead of creating partitions
until the first file system is full, the SPD Server randomly chooses
a file system from the DATAPATH= list for the first partition. Then,
it sequentially assigns partitions to successive file systems in the
DATAPATH= list. The software continues to cycle through the file system
set as many times as needed until all data partitions for the table
are stored.
Subsequently, you store
the BIGONE table in the domain. SPD Server uses random placement of
data partitions in the DATAPATH= list. The first BIGONE partition
can be stored in either the
/data1 or
the /data2 directory. Subsequent partitions
alternate between the /data1 and /data2 directories,
and so on.
If you set PARTSIZE=0,
SPD Server uses the DATAPATH= file systems strictly for overflow.
It creates partitions in the first file system, up to the file size
limit of your operating system. When the first file system is full,
it proceeds to the second file system, and so on.
What happens when you
issue the first LIBNAME statement for a domain, but you do not specify
path options? If your tables are small, the primary file system is
probably adequate. However, if your tables are large, the primary
file system can fill up quickly. When the primary file system is full,
SPD Server returns an error message when you perform an Append operation
on an existing table, or when you create a new table in the domain.
If the primary file
system is full, you can issue a subsequent LIBNAME statement that
specifies additional paths. You can append to an existing table, but
you might not be able to create a new table in the domain. The software
cannot store the first metadata file partition because the primary
file system is still full. What is the solution? You need to either
free space in the primary file system or get the SPD Server administrator
to create a new LIBNAME domain.
Using Path Options for Large Table Storage
Overview of Using Path Options
If you must manage your
table storage, anticipate disk space for large tables. Use the LIBNAME
path options with the first LIBNAME statement for the domain. To store
data and index partitions, use the DATAPATH= and INDEXPATH= options
on a different storage device other than the primary file system.
By using a different storage device, you reserve the primary file
system for metadata files.
Scenario for Using Path Options
In this example, the
SPD Server administrator has already created the primary file system
for MYLIB.
-
SITEUSR1 issues the first LIBNAME statement for the MYLIB domain. By default, the domain's primary file system is used to store metadata partitions. SITEUSR1 specifies another device (MYDISK30) and directory (SITEUSER) to store the data and index partitions.
/* I anticipate the primary file system for the MYLIB domain */ /* is ample for metadata files, but I will use MYDISK30 */ /* to store my data and index partitions. */ LIBNAME myref sasspds 'mylib' datapath=('/mydisk30/siteuser') indexpath=('/mydisk30/siteuser') server=husky.spdsname user='siteusr1' prompt=yes; -
SITEUSR1 issues a subsequent LIBNAME statement for the MYLIB domain and specifies additional paths for the data and index partitions. The user is storing large tables, so the list specifies two storage devices and directories for the data. SITEUSR1 also specifies a third device for indexes that are associated with the tables.
/* I noticed today MYDISK30 is getting full. */ /* I am adding MYDISK31 for possible overflow. */ LIBNAME expand sasspds 'mylib' datapath=('/mydisk31/siteuser' '/mydisk32/siteuser') indexpath=('/mydisk33/siteuser') server=husky.spdsname user='siteusr1' prompt=yes; -
Append the new paths to the existing list for each component type. The following path list is maintained by spdslibll:
datapath=('mydisk30/siteuser' '/mydisk31/siteuser' '/mydisk32/siteuser') indexpath=('mydisk30/siteuser' '/mydisk33/siteuser')SPD Server stores partitions of the data components for MYLIB tables in the specified data paths. (How the software uses the data paths depends on the value of the PARTSIZE= option.) For index components, SPD Server stores partitions in the first path in the list until that space is full, and then it proceeds to the next path in the list.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.