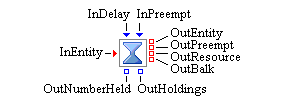
The Delay block delays the progression of an entity through a simulation model. When an entity enters a Delay block via its InEntity port, the Delay block pulls a value (the delay time) from its InDelay port. If the delay time value is not a number, the simulation terminates. If the value is less than 0, the Delay block logs a warning and uses a value of 0. The Delay block holds the entity for the duration of the delay time and then releases it through its OutEntity port. If the push through the OutEntity port fails, the Delay block attempts to push the entity out the OutBalk port. If this is not successful, the entity is destroyed and a message is posted to the Tracer.
Entities in Simulation Studio are hierarchical. That is, entities can hold other entities. The term controlling entity denotes an entity that holds other entities, and the term root entity denotes an entity that is not held by another entity. Each entity held by another entity has one root entity associated with it. The root entity for any held entity is found by traversing up the entity hierarchy from the held entity.
Entities being held by a Delay block can be preempted either by input to the block’s InPreempt port or by a scheduled resource entity event. In order for a root entity that is held by a Delay block to be preempted, the OutPreempt port (or OutBalk port) must have at least one link attached to it. Similarly, for a resource entity that is held by a controlling entity that is in turn held by the Delay block to be preempted, the OutResource port (or OutBalk port) must have at least one link connected to it.
The Delay block’s InPreempt port accepts an Entity Group object as input. (An Entity Group is a collection of references to entities.) When an Entity Group object is pushed to a Delay block’s InPreempt port, the Delay block iterates through the Entity Group collection looking for matches to root entities held by the Delay block. For any matched entity, the Delay block first tries to push that entity out its OutPreempt port. If this push is not successful, the block attempts to push the entity out the OutBalk port. If this also fails, the entity continues to be held by the Delay block until either it exits out the OutEntity port or it is preempted again.
The Delay block, like all entity holding blocks, detects potential preemptive changes (such as those scheduled by a Resource Scheduler block) to resource entities it holds (either directly or indirectly through a controlling entity).
If the number of units associated with a held resource entity decreases or the state of a held resource entity becomes nonfunctional, the Delay block attempts to preempt that resource entity. If the resource entity identified for preemption is a root entity, then the Delay block follows the same protocol for pushing an entity out its OutPreempt port that the InPreempt port uses. If the resource entity is part of a controlling entity, the Delay block removes the resource entity from the controlling entity and attempts to push the associated root entity out the OutPreempt port. The Delay block then attempts to push the preempted resource entity out its OutResource port, or if that fails, out its OutBalk port. If there is a connection to the Delay block’s OutResource port and the Delay block cannot push the resource entity out either the OutResource or OutBalk port, the resource entity is disposed.
The Delay block also provides an OutHoldings port that other blocks can use to pull an Entity Group object that contains a collection of references to entities held by the Delay block.
- InEntity
-
Input entity port for entities to be added to the Delay block.
- OutEntity
-
Output entity port for entities that can be accepted by a downstream block.
- OutPreempt
-
Output entity port for root entities that are preempted and can be accepted by a downstream block.
- OutResource
-
Output entity port for resource entities held by controlling entities that are preempted and can be accepted by a downstream block.
- OutBalk
-
Output entity port for entities that cannot leave using the other output entity ports.
- InDelay
-
Input numeric port for how long the Delay block should delay the next entity.
- InPreempt
-
Entity Group input port that causes the Delay block to preempt any root entities it is holding that match entities in the incoming Entity Group.
- OutHoldings
-
Entity Group output port from which a group of entity references can be pulled, representing the entities held by the Delay block.