Providers of Encryption
SAS Proprietary Encryption
SAS Proprietary Encryption Overview
SAS Proprietary Encryption
is licensed with Base SAS software and is available in all deployments.
It requires no additional SAS product licenses. The SAS Proprietary
algorithm is strong enough to protect your data from casual viewing. SAS/SECURE and TLS provide a higher level of security.
There are two types
of SAS Proprietary Encryption algorithms.
Refer to the SAS 9.4 Intelligence Platform:
Security Administration Guide, “Encryption for
Data at Rest” and “Encryption for Data in Motion”
chapters for detailed information.
-
A 32-bit rolling-key encryption algorithm that is used for SAS data set encryption with passwords.This encryption technique uses parts of the passwords that are stored in the SAS data set as part of the 32-bit rolling key encoding of the data. This encryption provides a medium level of security. Users must supply the appropriate passwords to authorize their access to the data, but with the speed of today’s computers, it could be subjected to a brute force attack on the 2,563,160,682,591 possible combinations of valid password values, many of which must produce the same 32-bit key.Note: SAS/SECURE and data set support of AES, which is also shipped with Base SAS software, provides a higher level of security.For detailed information, see SAS Data File Encryption in SAS Language Reference: Concepts.
-
A 32-bit fixed-key encoding used to protect passwords used for communications in configuration files, passwords for login objects, login passwords, internal account passwords, and so on.This SAS Proprietary algorithm is strong enough to protect your data from casual viewing. It provides a medium level of security. SAS/SECURE and TLS provide a higher level of security.Note: SAS recommends that you use the highest levels of security possible.Data-in-motion passwords that use SASProprietary encoding are passwords in transit in a logon attempt and general traffic between clients and servers. Depending on the type of client or server, higher levels of password security can be used. For example, TLS or AES can be used.Data-at-rest passwords are secured in the following ways.
-
Login passwords on-disk in the metadata can use SASProprietary (SAS002) or AES (SAS003 or SAS004). By default, metadata stores passwords on login objects with SAS003, but returns passwords using SAS002 by default.
-
Internal account passwords on-disk in the metadata can use MD5 or SHA-256 hashing. By default, SHA256 is used.Note: If SAS/SECURE is not present, MD5 is used. If MD5 hashing is specified in the configuration file, it overrides the default SHA-256 hashing.
-
Passwords on-disk in configuration files can use SASProprietary or AES. By default, SASProprietary (SAS002) is used.
Note: Configuration file passwords can be upgraded to AES (SAS003 or SAS004). SAS003 uses a 256-bit key plus 16-bit salt value to encode passwords. SAS004 uses a 256-bit key plus 64-bit salt value to encode passwords. -
SAS Proprietary Encryption System Requirements
SAS supports SAS Proprietary
Encryption under these operating environments:
-
UNIX
-
Windows
-
z/OS
SAS Proprietary Encryption Software Availability
SAS Proprietary Encryption
is licensed with Base SAS software and is available in all deployments.
It requires no additional SAS product licenses.
SAS Proprietary Encryption Installation and Configuration
SAS Proprietary Encryption
is part of Base SAS. Separate installation is not required.
Configure SAS Proprietary
Encryption as follows:
-
SAS Proprietary Encryption for SAS data sets is implemented with the ENCRYPT= data set option set to YES. You can use the ENCRYPT= data set option only when you are creating a SAS data file. You must also assign a password when encrypting a data file with SAS Proprietary Encryption. At a minimum, you must specify the READ= data set option or the PW= data set option at the same time you specify ENCRYPT=YES. Because passwords are used in this encryption technique, you cannot change any password on an encrypted data set without re-creating the data set.Note: Beginning with the first maintenance release of 9.4, a metadata-bound library administrator can require that all data files in the bound library be encrypted with either AES or SAS Proprietary encryption. For more information, see Requiring Encryption for Metadata-Bound Data Sets in Base SAS Procedures Guide and SAS Guide to Metadata-Bound Libraries.For detailed information, see SAS Data File Encryption in SAS Language Reference: Concepts.
-
SAS Proprietary Encryption for communications and networking is implemented by setting system option NETENCRYPTALGORITHM=SASPROPRIETARY. The NETENCRYPTALGORITHM= option must be set before the LIBNAME statement establishes the connection to the server. On the server, you set the NETENCRYPT option to specify that encryption is required by any client that accesses this server. The NETENCRYPTALGORITHM= option specifies that the SASProprietary algorithm be used for encryption of all data that is exchanged with connecting clients.For detailed information, see NETENCRYPT System Option and NETENCRYPTALGORITHM System Option.
For
an example of configuring and using SAS Proprietary Encryption in
your environment, see SAS Proprietary Encryption for SAS/SHARE: Example . For
an example of configuring SAS Data File encryption using the SASProprietary
algorithm, see SAS Data File Encryption in SAS Language Reference: Concepts.
SAS/SECURE
SAS/SECURE Overview
SAS/SECURE software provides industry standard encryption capabilities in addition to the SASProprietary
algorithm.
On UNIX, Windows, and z/OS, SAS/SECURE supports the following encryption algorithms:
-
SASProprietary
-
RC2
-
RC4
-
DES
-
TripleDES
-
AES
Note: The algorithms listed above
are supported by SAS/SECURE on Windows by using the Microsoft Cryptographic
API libraries that are included with the operating system.
Refer to Encryption Algorithms for more information
about encryption algorithms supported for use with SAS/SECURE.
SAS/SECURE provides
encryption for the following:
-
data in transitSAS/SECURE enables you to provide stronger protection for data in transit than is provided by SAS Proprietary Encryption. This affects communications among SAS servers and between SAS servers, SAS desktop clients, and SAS web applications.Refer to NETENCRYPT System Option and NETENCRYPTALGORITHM System Option for details.
-
stored login passwordsSAS/SECURE also enables you to provide stronger protection for stored login passwords than is provided by SAS Proprietary encoding. By default, the stored login passwords are stored using SAS002 encoding. With SAS/SECURE, you can use SAS003 or SAS004 encoding methods, which use industry-standard algorithms for stored passwords. The SAS003 encoding method uses AES with 16-bit salt and the SAS004 encoding method uses AES with 64-bit salt. You can use the PWENCODE procedure (specify the METHOD= option) to upgrade to stronger encryption, AES (SAS003 or SAS004).Refer to PWENCODE Procedure for details.
-
internal account passwords stored in the metadata repositorySAS/SECURE also enables you to provide stronger protection for internal account passwords stored in the metadata repository. You should use a minimum of SHA-256 hashing.CAUTION:Passwords that are stored in SAS003 format, SAS004 format, or SHA-256 hashing become unusable and inaccessible if SAS/SECURE is unavailable. If you choose to discontinue use of SAS/SECURE, you must revert stored passwords to the less secure format before you discontinue using the software.
-
services that are part of the Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) 140-2 standardYou can instruct SAS/SECURE to use only services that are part of the Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) 140-2 standard. When SAS system option ENCRYPTFIPS is configured, SAS/SECURE uses only FIPS 140-2 validated encryption and hashing algorithms from libraries that are validated when loaded. AES is the encryption algorithm and SAS003 is the encoding format (for stored passwords) used with FIPS 140-2 enabled SAS/SECURE software. The SHA-256 hashing algorithm is used with FIPS 140-2 enabled software for stored internal account passwords in the metadata server.Refer to How SAS Implements FIPS.ENCRYPTFIPS System OptionAlso see and SAS/SECURE FIPS 140-2 Compliant Installation and Configuration for details.
-
AES Encryption on Data SetsAES encryption on SAS Data Files is available in SAS 9.4. AES produces a stronger encryption by using a key value that can be up to 64 characters long. You specify ENCRYPT=AES when creating a data set. Instead of passwords that are stored in the data set (SAS Proprietary Encryption), AES uses a key value that is not stored in the data set. You must use the ENCRYPTKEY= data set option when creating or accessing an AES encrypted data set unless the metadata-bound library administrator has securely recorded the encryption key in metadata to which the data set is bound. You cannot change the ENCRYPTKEY= key value on an AES encrypted data set without re-creating the data set.Note: Beginning with the first maintenance release of 9.4, a metadata-bound library administrator can require that all data files in the bound library be encrypted with either AES or SAS Proprietary encryption. For more information, see Requiring Encryption for Metadata-Bound Data Sets in Base SAS Procedures Guide and SAS Guide to Metadata-Bound Libraries.For detailed information about AES Encryption on SAS Data Files, see AES Encryption in SAS Language Reference: Concepts.
SAS/SECURE System Requirements
SAS supports SAS/SECURE
under these operating environments:
-
UNIX
-
Windows
-
z/OS
SAS/SECURE Software Availability
For software delivery
purposes, SAS/SECURE is a product within the SAS System. In SAS 9.4,
SAS/SECURE is included with the Base SAS software. In prior releases,
SAS/SECURE was an add-on product that was licensed separately. This change makes strong encryption
available in all deployments (except where prohibited by import restrictions).
SAS/SECURE Export Restrictions
For U.S. export purposes, SAS designates each product based on the encryption algorithms
and the product's functional capability. SAS/SECURE is available to most commercial and government users
inside and outside the U.S. However, some countries (for example,
Russia, China, and France) have import restrictions on products that
contain encryption, and the U.S. prohibits the export of encryption
software to specific embargoed or restricted destinations.
SAS/SECURE for UNIX, Windows, and z/OS includes the following encryption algorithms:
-
RC2 using up to 128-bit keys
-
RC4 using up to 128-bit keys
-
DES using up to 56-bit keys
-
TripleDES using up to 168-bit keys
-
AES using 256-bit keys
SAS/SECURE for Windows uses the encryption algorithms that are available in Microsoft CryptoAPI.
The level of the SAS/SECURE
encryption algorithms under Windows depends on the level of the encryption
support in Microsoft CryptoAPI under Windows.
Note: For AES, SAS does not use
Windows libraries by default. It tries to use the RSA libraries that
are FIPS certified.
SAS/SECURE Installation and Configuration
SAS/SECURE is now installed and delivered on every installation.
Whether SAS/SECURE is used depends on the options that are set.
In SAS 9.4, SAS/SECURE is installed with the Base SAS software. However, the default encryption is now SAS
Proprietary Encryption.
To use the higher form of encryption provided by SAS/SECURE for communications and networking, specify the NETENCRYPT system option and set the
NETENCRALG= system option to a value of RC2, RC4, DES, TRIPLEDES, AES, or SSL. Refer to NETENCRYPT System Option and NETENCRYPTALGORITHM System Option.
For examples of configuring
and using SAS/SECURE
with SAS/CONNECT and SAS/SHARE, see Encryption Technologies: Examples.
For
detailed information about AES Encryption on SAS Data Files, see AES Encryption in SAS Language Reference: Concepts.
SAS/SECURE FIPS 140-2 Compliant Installation and Configuration
To configure a FIPS
140-2 compliant system, you must use SAS/SECURE or TLS. When using SAS/SECURE, specify SAS system
options ENCRYPTFIPS and NETENCRALG= (set to AES) for UNIX, z/OS, or Windows. When using TLS, specify SAS system options ENCRYPTFIPS and NETENCRALG=
(set to AES or SSL) for UNIX, z/OS, or Windows. Therefore, you can connect only servers and clients that are also configured
with AES or SSL. Errors are generated when other encryption algorithms are specified.
When ENCRYPTFIPS is specified, an INFO message is written at server start-up to indicate
that FIPS encryption is enabled.
In the FIPS 140-2 compliant
mode, the SHA-256 hashing algorithm is used for stored password protection.
Therefore, you can connect only servers and clients that are enabled
for FIPS 140-2.
CAUTION:
In SAS
9.2, the password hash list was created using the MD5 hash algorithm.
If you are moving from SAS 9.2 to a higher version of SAS and configuring
your system to be FIPS 140-2 compliant, you need to clear all previously
stored passwords. When you reset the passwords, they use the SHA-256
hashing algorithm.
See the following information
for details about FIPS.
Transport Layer Security (TLS)
Transport Layer Security (TLS) Overview
Transport Layer Security (TLS) and its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), are cryptographic protocols that are designed to provide communication security.
TLS and SSL are protocols that provide network data privacy, data integrity, and authentication.
Note: All discussion of TLS is
also applicable to the predecessor protocol, Secure Sockets Layer
(SSL).
TLS uses X.509 certificates and hence asymmetric cryptography to assure the party with whom they are communicating, and to exchange a symmetric
key. As a consequence of choosing X.509 certificates, certificate authorities and
a public key infrastructure are necessary to verify the relation between a certificate and its
owner, as well as to generate, sign, and administer the validity of certificates.
For more information
about client and server negotiations using certificates, refer to Certificate Implementation: How TLS Client and Servers Negotiate.
In addition to providing encryption services, TLS performs client and server authentication,
and it uses message authentication codes to ensure data integrity. The client requests
a certificate from the server, which it validates against the public certificate of
the certificate authority used to sign the server certificate. The client then verifies
the identity of the server and negotiates with the server to select a cipher (encryption
method). The cipher that is selected is the first match between the ciphers that are
supported on both the client and the server. All subsequent data transfers for the
current request are then encrypted with the selected encryption method.
TLS Concepts
The following concepts are fundamental to understanding TLS:
Certificate Authorities (CAs)
Cryptography products provide security services by using digital certificates, public-key cryptography, private-key cryptography, and digital signatures. Certificate authorities (CAs)
create and maintain digital
certificates, which also help preserve confidentiality.
Various commercial
CAs, such as VeriSign and Thawte, provide competitive services for
the e-commerce market. You can also develop your own CA by using products
from companies such as RSA Security and Microsoft or from the Open-Source
Toolkit OpenSSL.
Note: z/OS provides the PACDCERT
command and PKI Services for implementing a CA.
Digital Signatures
A digital signature affixed to an electronic document or to a network data packet is like a personal
signature that concludes a hand-written letter or that validates a credit card transaction.
Digital signatures are a safeguard against fraud. A unique digital signature results
from using a private key to encrypt a message digest. A document that contains a digital signature enables
the receiver of the document to verify the source of the document. Electronic documents
are said to be verified if the receiver knows where the document came from, who sent
it, and when it was sent.
Another form of verification
comes from Message Authentication Codes (MAC), which ensure that a
signed document has not been changed. A MAC is attached to a document
to indicate the document's authenticity. A document that contains
a MAC enables the receiver of the document (who also has the secret
key) to know that the document is authentic.
Digital Certificates
Digital certificates are electronic documents that ensure the binding of a public
key to an individual or an organization. Digital certificates provide protection
from
fraud.
Usually, a digital certificate contains a public key, a user's name, and an expiration date. It also contains the
name of the Certificate
Authority (CA) that issued the digital certificate and a digital signature that is
generated by the CA. The CA's validation of an individual or an organization
allows that individual or organization to be accepted at sites that trust the CA.
Public and Private Keys
Public-key cryptography uses a public and a private key pair. The public key can be
known by anyone, so anyone can send a confidential message. The private key
is confidential and known only to the owner of the key pair, so only the owner can
read the encrypted message. The public key is used primarily for encryption, but it
can also be used to verify digital signatures. The private key is used primarily
for decryption, but it can also be used to generate a digital signature.
Symmetric Key
In symmetric key encryption, the same key is used to encrypt and decrypt the message.
If two parties want to
exchange encrypted messages securely, they must both have a copy of the same symmetric
key. Symmetric key cryptography is often used for encrypting large amounts of data
because it is computationally
faster than asymmetric cryptography. Typical algorithms include DES, TripleDES, RC2,
RC4, and AES.
Asymmetric Key
Asymmetric or public key encryption uses a pair of keys that have been derived together
through a complex mathematical
process. One of the keys is made public, typically by asking a CA to publish the public
key in a certificate for the certificate-holder (also called the subject). The private
key is kept secret by the subject and never revealed to anyone. The keys work together
where one is used to perform the inverse operation of the other: If the public key
is used to encrypt data, only the private key of the pair can decrypt it. If the private
key is used to encrypt, the public key must be used to decrypt. This relationship
allows a public key encryption scheme where anyone can obtain the public key for a
subject and use it to encrypt data that only the user with the private key can decrypt.
This scheme also specifies that when a subject encrypts data using its private key,
anyone can decrypt the data by using the corresponding public key. This scheme is
the foundation for digital signatures.
TLS System Requirements
SAS supports TLS under these operating environments:
-
UNIX
-
Windows
-
z/OS
Note: The TLS software is included
in the SAS installation software only for countries that allow the
importation of encryption software.
TLS Software Availability
In the fourth
maintenance release of SAS 9.4, the OpenSSL libraries
provided by SAS have been updated. For SAS 9.4 and all maintenance
releases of SAS 9.4, updated versions of OpenSSL are provided and
updated through hot fixes. See the SAS Security Bulletin on OpenSSL for
the most current information about the versions of OpenSSL used in
SAS products and about the advisories under consideration.
For a quick reference
of the OpenSSL version supported for each version of SAS Foundation,
see Mapping Between SAS Version and OpenSSL Version.
The TLS version supported by default is now TLS 1.2.
Note: If you need to override the
default protocol, you can set the SAS_SSL_MIN_PROTOCOL= environment
variable. For information, see SAS_SSL_MIN_PROTOCOL Environment Variable.
OpenSSL is shipped with
Base SAS for UNIX and z/OS. Windows versions of SAS support the TLS versions that Windows supports.
SAS deployments on Windows,
UNIX, and z/OS platforms can be configured to use TLS. The implementation and file extensions,
however, vary based on the operating system.
-
For Windows, SAS uses the SChannel library that comes with the Windows operating system.
-
SAS provides the libraries needed to run TLS on UNIX. To find the OpenSSL code base version that is used to build the TLS libraries provided by SAS for each release, see Mapping Between SAS Version and OpenSSL Version.Note: Different operating systems require the use of different library file extensions. For example, HPUX, Linux, and Solaris use libcrypto.so.1.0.0 and libssl.so.1.0.0. AIX uses libcrypto.so and libssl.so. Refer to your operating system vendor documentation when using the vendor’s OpenSSL libraries. There might be additional procedures that need to be followed to make the libraries work properly in your environment.
-
SAS provides the libraries needed to run TLS on z/OS.
TLS Installation and Configuration
TLS for UNIX, z/OS, and Windows is shipped with Base
SAS. No additional software installation is required. For SAS 9.4
and all maintenance releases of SAS 9.4, updated versions of OpenSSL
are provided and updated through hot fixes. See OpenSSL Security Advisories for the
latest information about OpenSSL security advisories under consideration
for software fixes for SAS components.
In the third maintenance
release of SAS 9.4, the SAS Deployment Manager used to automate the
process of adding and removing intermediate, root, or self-signed
CA certificates. At installation, a list of CA certificates that are
distributed by Mozilla software products is installed in the cacerts.pem
and trustedcerts.pem files. The SAS Deployment Manager is then used
to add existing certificates to the Trusted CA Bundle and to remove
digital certificates from the Trusted CA Bundle.
In the third maintenance
release of SAS 9.4, this new trusted certificate list is a file in
X.509 Base-64 encoded format and is named trustedcerts.pem. System
option SSLCALISTLOC= points to the location of this file, which is
now
<SASHome>/SASSecurityCertificateFramework/1.1/cacerts/trustedcerts.pem.
The instructions that you use to configure TLS at your site depend on whether you
use UNIX, Windows, or z/OS. See the appropriate details:
For examples of configuring and using TLS in your environment, see Encryption Technologies: Examples.
TLS: FIPS 140-2 Compliant Installation and Configuration
You can configure TLS to run in FIPS 140-2 compliant mode. The libraries supplied
by Windows are FIPS 140-2
compliant. The OpenSSL libraries shipped with SAS for UNIX are not FIPS 140-2 compliant.
However, you can compile a FIPS 140-2 compliant version of OpenSSL and install it.
For more information,
see TLS on UNIX: Building FIPS 140-2 Capable OpenSSL and TLS on Windows: FIPS 140-2 Capable OpenSSL .
After compiling the FIPS compliant libraries, you will need to specify the NETENCRALG=
(set to AES or SSL) system option. You will then be able to run in FIPS compliant
mode and connect only
servers and clients that are also configured with FIPS.
CAUTION:
Use ENCRYPTFIPS
with caution.
Turning on the ENCRYPTFIPS option is not generally recommended for TLS, unless absolutely
required by your site’s policy. If the ENCRYPTFIPS option is turned
on, the SAS server-based TLS clients will attempt to load a special subset of OpenSSL
libraries, contained as part of the OpenSSL FIPS Object Module. Because these libraries
are not present by default, you must follow the process described in TLS on UNIX: Building FIPS 140-2 Capable OpenSSL .
When ENCRYPTFIPS is specified, an INFO message is written at server start-up to indicate
that FIPS encryption is enabled.
Note: The TLS version shipped with
SAS for z/OS is not FIPS 140-2 compliant. However, you can use SAS/SECURE
with AES to provide FIPS on z/OS.
See the following for
more information about FIPS.
SSH (Secure Shell)
SSH (Secure Shell) Overview
SSH is an abbreviation for Secure Shell. SSH is a protocol that enables users to access a remote computer via a secure connection.
SSH is available through various commercial products and as freeware. OpenSSH is a
free version of the SSH protocol suite of network connectivity tools.
Although SAS software does not directly support SSH functionality, you can use
the tunneling feature of SSH to enable data to flow between a SAS client and a SAS server. Port
forwarding is another term for tunneling. The SSH client and SSH server act as agents
between the SAS client and the SAS server, tunneling information via the SAS client's
port to the SAS server's port.
Only Windows and UNIX
operating systems can access an OpenSSH server on another UNIX system.
To access an OpenSSH server, UNIX systems require OpenSSH software.
Windows systems require
PuTTY software.
Currently, SAS supports the OpenSSH client and server that supports protocol level
SSH-2 in UNIX environments. Other third-party applications that support the SSH-2
protocol
currently are untested. Therefore, SAS does not support these applications.
SAS also supports SSH on z/OS. The IBM Ported Tools for z/OS Program Product must be installed
for OpenSSH support. See IBM Ported Tools for z/OS - OpenSSH.
To understand the configuration
options that are required for the OpenSSH and PuTTY clients and the
OpenSSH server, it is recommended that you have a copy of the book SSH,
The Secure Shell: The Definitive Guide by Daniel J. Barrett, Richard E. Silverman, and Robert G. Byrnes. This book is an
invaluable resource when you are configuring the SSH applications, and it describes
in detail topics that include public key authentication, SSH agents, and SSHD host
keys.
SSH System Requirements
SAS supports SSH in these operating environments:
-
UNIX
-
Windows
-
z/OS
SSH Software Availability
OpenSSH supports SSH protocol versions 1.3, 1.5, and 2.0.
To build the OpenSSL
software, refer to the following resources:
-
SSH UNIX manual page
-
Barrett, Daniel J., Richard E. Silverman, and Robert G. Byrnes. 2005. SSH, the Secure Shell: The Definitive Guide. Sebastopol, CA: O'Reilly
SSH Tunneling Process
An inbound request from a SAS client to a SAS server
is shown as follows:
SSH Tunneling Process
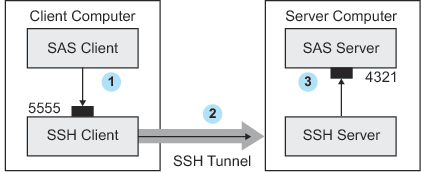
-
The SAS client passes its request to the SSH client's port 5555.
-
The SSH client forwards the SAS client's request to the SSH server via an encrypted tunnel.
-
The SSH server forwards the SAS client's request to the SAS server via port 4321.
Outbound, the SAS server's reply to the SAS client's request flows from the SAS server
to the SSH server. The SSH server forwards the reply to the SSH client, which passes
it to the
SAS client.
SSH Tunneling: Process for Installation and Setup
SSH software must be installed on the client and server computers. Exact details
about
installing SSH software at the client and the server depend on the particular brand
and version of the software that is used. See the installation instructions for your
SSH software.
The process for setting
up an SSH tunnel consists of the following steps:
-
SSH tunneling software is installed on the client and server computers. Details about tunnel configuration depend on the specific SSH product that is used.
-
On UNIX, you use OpenSSH software to access your UNIX OpenSSH server.
-
On Windows, you use PuTTY software to access your UNIX OpenSSH server.
-
On z/OS, the IBM Ported Tools for z/OS Program Product must be installed for OpenSSH support.
-
-
The SSH client is started as an agent between the SAS client and the SAS server.
-
The components of the tunnel are set up. The components are a listen port, a destination computer, and a destination port. The SAS client accesses the listen port, which is forwarded to the destination port on the destination computer. SSH establishes an encrypted tunnel that indirectly connects the SAS client to the SAS server.
For examples of setting
up and using a tunnel, see SSH Tunnel for SAS/CONNECT: Example and SSH Tunnel for SAS/SHARE: Example .
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All Rights Reserved.