| CUSUMARL Function |
computes the average run length for a cumulative sum control chart scheme.
Syntax
CUSUMARL(type,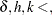 headstart>)
headstart>)
where
type |
indicates a one-sided or two-sided scheme. Valid values are 'ONESIDED' or 'O' for a one-sided scheme, and 'TWOSIDED' or 'T' for a two-sided scheme. |
|
is the shift to be detected, expressed as a multiple of the process standard deviation |
|
is the decision interval (one-sided scheme) or the vertical distance between the origin and the upper arm of the V-mask (two-sided scheme), each time expressed as a positive value in standard units (a multiple of |
|
is the reference value (one-sided scheme) or the slope of the lower arm of the V-mask (two-sided scheme), each time expressed as a positive value in standard units (a multiple of |
headstart |
is the headstart value (optional) expressed in standard units (a multiple of |
Description
The CUSUMARL function returns the average run length of one-sided and two-sided cumulative sum schemes with parameters as described above. The notation is consistent with that used in the CUSUM procedure.
For a one-sided scheme, the average run length is calculated using the integral equation method (with 24 Gaussian points) described by Goel and Wu (1971) and Lucas and Crosier (1982).
For a two-sided scheme with no headstart, the average run length (ARL) is calculated using the fact that
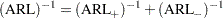 |
where ARL and ARL
and ARL denote the average run lengths of the equivalent one-sided schemes for detecting a shift of the same magnitude in the positive direction and in the negative direction, respectively.
denote the average run lengths of the equivalent one-sided schemes for detecting a shift of the same magnitude in the positive direction and in the negative direction, respectively.
For a two-sided scheme with a nonzero headstart, the ARL is calculated by combining average run lengths for one-sided schemes as described in Appendix A.1 of Lucas and Crosier; 1982, p. 204.
For a specified shift 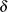 , you can use the CUSUMARL function to design a cusum scheme by first calculating average run lengths for a range of values of
, you can use the CUSUMARL function to design a cusum scheme by first calculating average run lengths for a range of values of 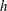 and
and 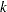 and then choosing the combination of
and then choosing the combination of 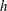 and
and 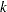 that yields a desired average run length.
that yields a desired average run length.
You can also use the CUSUMARL function to interpolate published tables of average run lengths.
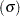 .
. 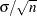 , where
, where  is the subgroup sample size).
is the subgroup sample size).