Probability of Default Model Validation Reports
About Probability of Default Model Validation Reports
Probability of Default (PD) models help validate the stability, performance, and calibration of models with the following statistical measures and tests:
Model stability measures
The model stability
measures track the change in distribution of the modeling data and
the scoring data.
Model performance measures
The model performance measures report this information:
-
The model’s ability to discriminate accounts that have defaulted with those that have not defaulted. The score difference between the accounts that default and those that do not helps determine the cut-off score, which is used to predict whether a credit exposure is a default.
-
The relationship between the actual default probability and the predicted probability. This information is used to understand a model’s performance over a period of time.
Model calibration measures
The model calibration measures check the accuracy of the PD model by comparing the
correct quantification
of the risk components with the available standards.
For a description of
the statistical measures, see Statistical Measures Used in Basel III Reports.
Default Model Validation Report Properties
In order to create the
reports, SAS Model Manager must know the input and output variables for the model. To run the reports, the New Report window requires the name of an input table. The input table can contain only input variables, or it can contain input and output variables. If the input table contain only input
variables only, a scoring test must be run to obtain the output variable. If the input table contains the input and output variables, no scoring is necessary.
You specify whether a scoring test must be run by setting the Run
score code property in the New Report window.
If the input table contains the input and output variables, the value
of the Run score code can be No.
If the input table contains only input variables, the Run
score code property must be set to Yes.
The report properties require the names of the variables from the input and output tables in order to map these variables to variables that are used to create the reports.
The report properties map these variables:
| Time period variable | specifies the variable that is used to indicate a time period. The first time period begins with 1 and typically increments by 1. The default is period. |
| Time label variable | (optional) specifies a label for the time period. If this variable exists in the input table, the report output contains a table that maps time periods to time labels. |
| Scorecard bin variable | specifies the scoring output variable that names the scorecard bins. The input table must include this variable if scoring for the PD report is performed outside SAS Model Manager. If scoring is done by SAS Model Manager, do not include this variable in the input data set. The default is scorecard_bin. |
| Scorecard points variable | specifies the scoring output variable that names the scorecard points. The input table must include this variable if scoring for the PD report is performed outside SAS Model Manager. If scoring is done by SAS Model Manager, do not include this variable in the input data set. The default is scorecard_points. |
| Cut-off value | specifies the variable that is used to derive whether a credit exposure is a default. The cut-off value is also used to compute accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, precision, and error rate measures. You can use the score difference between accounts that default on loans and those that do not default on loans to determine the cut-off value. The default is 100. |
Prerequisites for Probability of Default Model Validation Reports
Before you can create a Probability of Default Model Validation report, verify that
the following project settings are specified and that the output variables have been
mapped:
Training target variable
Specifies the name of the target variable that was used to train the model. The model must have the same training target variable
as the project.
Class target level
Specifies a Binary class target level.
Output event probability variable
Specifies the name
of the output event probability variable.
Create a Probability of Default Model Validation Report
To create a Probability
of Default Model Validation report:
-
Click
 and select Probability of Default Model
Validation. The New Report window
appears.
and select Probability of Default Model
Validation. The New Report window
appears.
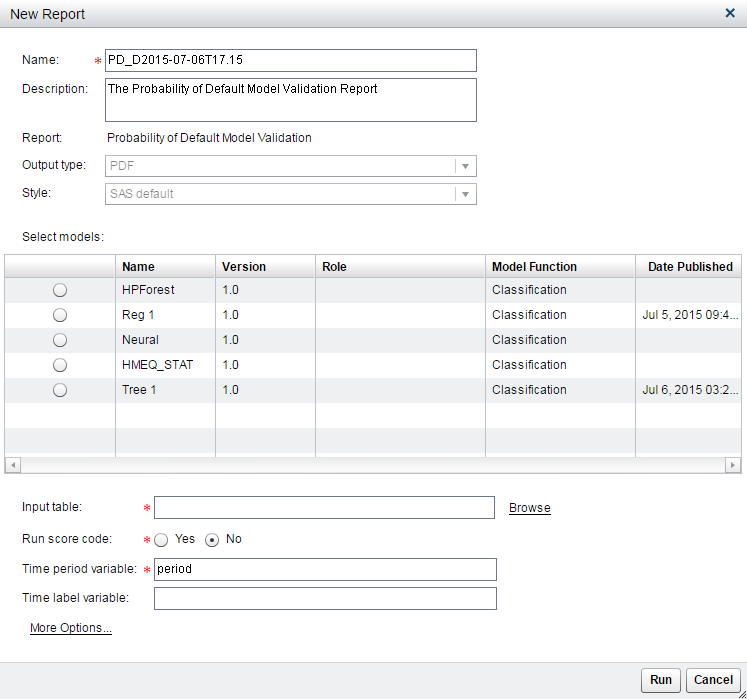
-
Enter a name and description if you do not want to use the default values.Note: The default output type is PDF.
-
From the list, select the model that you want to include in the report.
-
Click Browse to navigate to the appropriate folder and select an input table and click OK. The table can contain only input variables or both input and output variables.Note: When a scoring input table for a PD report contains data and one or more time periods do not contain default or non-default loan information, these time periods are not used to calculate the PD measurements. In a chart, time periods that are not used to calculate the PD measurements are represented with dashed lines.
-
Select whether to run the score code. If the input table contains only input variables, set Run score code to Yes. If the input table contains input and output variables, set Run score code to No.
-
The Time period variable specifies the variable from the input table whose value is a number that represents the development period. This value is numeric. The time period for PD reports begin with 1. The default is period.
-
(Optional) In the Time label variable field, enter the variable from the input table that is used for time period labels. When you specify the time label variable, the report appendix shows the mapping of the time period to the time label.
-
Click More Options to set the following:Scorecard bin variableSpecifies the variable from the input table that contains the scorecard bins. If the scoring job for the PD report is run outside SAS Model Manager, the scorecard bin variable must be a variable in the input table. If scoring is done within SAS Model Manager, do not include the variable in the input table. The default is scorecard_bin.Scorecard points variableSpecifies the variable that contains the scorecard points. If the scoring job for the PD report is run outside SAS Model Manager, the scorecard points variable must be a variable in the input table. If scoring is done within SAS Model Manager, do not include the variable in the input table. The default is scorecard_points.Cut-off valueSpecifies the maximum value that can be used to derive the predicted event and to further compute accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, precision, and error rate. The default is 100.
-
Click Run. The report is generated and appears in the default viewer for the selected output type.
See Also
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Last updated: February 14, 2017