How Does the SAS LASR Analytic Server Work?
Distributed SAS LASR Analytic Server
The SAS LASR Analytic Server
provides a client/server environment where the client connects to
the server, sends requests to the server, and receives results back
from the server. The server-side environment is a distributed computing
environment. A typical deployment is to use a series of blades in
a cluster. In addition to using a homogeneous hardware profile, the
software installation is also homogeneous. The same operating system
is used throughout and the same SAS software is installed on each
blade that is used for the server. In order for the software on each
blade to share the workload and still act as a single server, the
SAS software that is installed on each blade implements the Message
Passing Interface (MPI). The MPI implementation is used to enable
communication between the blades.
After a client connection
is authenticated, the server performs the operations requested by
the client. Any request (for example, a request for summary statistics)
that is authorized will execute. After the server completes the request,
there is no trace of the request. Every client request is executed
in parallel at extraordinarily high speeds, and client communication
with the server is practically instantaneous and seamless.
There are two ways to
load data into a distributed server:
-
load data from tables and data sets. You can start a server instance and directly load tables into the server by using the SAS LASR Analytic Server engine or the LASR procedure from a SAS session that has a network connection to the cluster. Any data source that can be accessed with a SAS engine can be loaded into memory. The data is transferred to the root node and the root node distributes the data to the worker nodes. You can also append rows to an in-memory table with the SAS LASR Analytic Server engine.
-
load tables from a co-located data provider.
-
Tables can be read from the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) that is provided by SAS High-Performance Deployment of Hadoop. You can use the SAS Data in HDFS engine to add tables to HDFS. When a table is added to HDFS, it is divided into blocks that are distributed across the machines in the cluster. The server software is designed to read data in parallel from HDFS. When used to read data from HDFS, the LASR procedure causes the worker nodes to read the blocks of data that are local to the machine.
-
The following figure
shows the relationship of the root node, the worker nodes, and how
they interact when working with large data sets in HDFS. As described
in the previous list, the LASR procedure communicates with the root
node and the root node directs the worker nodes to read data in parallel
from HDFS. The figure also indicates how the SAS Data in HDFS engine
is used to transfer data to HDFS.
Relationship of PROC LASR and the SAS Data in HDFS Engine
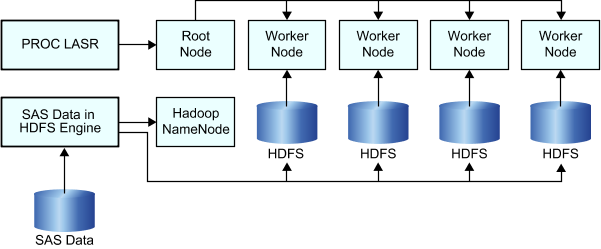
Note: The preceding figure shows
the distributed architecture of SAS High-Performance Deployment of Hadoop. For deployments
that use a third-party vendor database, the architecture is also distributed,
but different procedures and software components are used for distributing
and reading the data.
Non-Distributed SAS LASR Analytic Server
Most of the features
that are available with a distributed deployment also apply to the
non-distributed deployment too. Any limitations are related to the
reduced functionality of using a single-machine rather than a distributed
computing environment.
In a non-distributed
deployment, the server acts in a client/server fashion where the client
sends requests to the server and receives results back. The server
performs the analytic operations on the tables that are loaded in
to memory. As a result, the processing times are very fast and the
results are delivered almost instantaneously.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.