Introduction to In-Database Procedures
Using conventional
processing, a SAS procedure (by means of the
SAS/ACCESS engine) receives all the rows of the
table from the database. All processing is done by the procedure.
Large tables mean that a significant amount of data must be transferred.
Using the new in-database
technology, the procedures that are enabled for processing inside
the data source generate more sophisticated queries. These queries
allow the aggregations and analytics to be run inside the data source.
Some of the in-database procedures generate SQL procedure syntax and
use implicit pass-through to generate the native SQL. Other in-database
procedures generate native SQL and use explicit pass-through. For
more information about how a specific procedure works inside the data
source, see the documentation for that procedure.
The queries submitted
by SAS in-database procedures reference DBMS SQL functions and, in
some cases, the special SAS functions that are deployed inside the
data source. One example of a special SAS function is the SAS_PUT( )
function that enables you to execute PUT function calls inside the
data source. Other examples are SAS functions for computing sum-of-squares-and-crossproducts
(SSCP) matrices.
For most in-database
procedures, a much smaller result set is returned for the remaining
analysis that is required to produce the final output. As a result
of using the in-database procedures, more work is done inside the
data source, and less data movement can occur. This could result in
significant performance improvements.
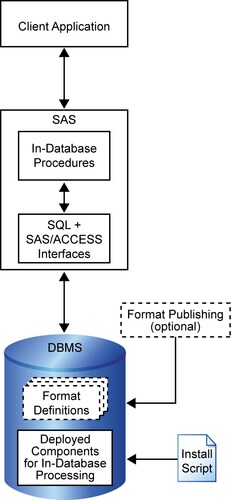
This diagram illustrates
the in-database procedure process.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.