Language Reference
References
-
Abramowitz, M., and Stegun, I. A., eds. (1972). Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables. 10th printing. New York: Dover.
-
Aiken, R. C. (1985). Stiff Computation. New York: Oxford University Press.
-
Al-Baali, M., and Fletcher, R. (1985). “Variational Methods for Nonlinear Least Squares.” Journal of the Operations Research Society 36:405–421.
-
Al-Baali, M., and Fletcher, R. (1986). “An Efficient Line Search for Nonlinear Least Squares.” Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications 48:359–377.
-
Ansley, C. F. (1979). “An Algorithm for the Exact Likelihood of a Mixed Autoregressive–Moving Average Process.” Biometrika 66:59–65.
-
Ansley, C. F. (1980). “Computation of the Theoretical Autocovariance Function for a Vector ARMA Process.” Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation 12:15–24.
-
Ansley, C. F., and Kohn, R. (1986). “A Note on Reparameterizing a Vector Autoregressive Moving Average Model to Enforce Stationary.” Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation 24:99–106.
-
Barnett, V., and Lewis, T. (1978). Outliers in Statistical Data. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Barreto, H., and Maharry, D. (2006). “Least Median of Squares and Regression through the Origin.” Computational Statistics and Data Analysis 50:1391–1397.
-
Barrodale, I., and Roberts, F. D. K. (1974). “Algorithm 478: Solution of an Overdetermined System of Equations in the
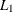 -Norm.” Communications of the ACM 17:319–320.
-Norm.” Communications of the ACM 17:319–320.
-
Bates, D. M., Lindstrom, M. J., Wahba, G., and Yandell, B. S. (1987). “GCVPACK-Routines for Generalized Cross Validation.” Communications in Statistics—Simulation and Computation 16:263–297.
-
Beale, E. M. L. (1972). “A Derivation of Conjugate Gradients.” In Numerical Methods for Nonlinear Optimization, edited by F. A. Lootsma, 39–43. London: Academic Press.
-
Beaton, A. E. (1964). The Use of Special Matrix Operations in Statistical Calculus. Princeton, NJ: Educational Testing Service.
-
Bickart, T. A., and Picel, Z. (1973). “High Order Stiffly Stable Composite Multistep Methods for Numerical Integration of Stiff Differential Equations.” BIT 13:272–286.
-
Bishop, Y. M. M., Fienberg, S. E., and Holland, P. W. (1975). Discrete Multivariate Analysis: Theory and Practice. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
-
Box, G. E. P., and Jenkins, G. M. (1976). Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control. Rev. ed. San Francisco: Holden-Day.
-
Breiman, L. (1995). “Better Subset Regression Using the Nonnegative Garrote.” Technometrics 37:373–384.
-
Brent, R. P. (1973). Algorithms for Minimization without Derivatives. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall. Chapter 5.
-
Brewer, C. A. (2013). “ColorBrewer 2.0: Color Advice for Cartography.” Accessed June 4, 2013. http://colorbrewer.org/.
-
Brockwell, P. J., and Davis, R. A. (1991). Time Series: Theory and Methods. 2nd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag.
-
Brownlee, K. A. (1965). Statistical Theory and Methodology in Science and Engineering. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Charnes, A., Frome, E. L., and Yu, P. L. (1976). “The Equivalence of Generalized Least Squares and Maximum Likelihood Estimation in the Exponential Family.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 71:169–171.
-
Christensen, R. (1997). Log-Linear Models and Logistic Regression. 2nd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag.
-
Chung, C. F. (1996). “A Generalized Fractionally Integrated ARMA Process.” Journal of Time Series Analysis 2:111–140.
-
Cox, D. R., and Hinkley, D. V. (1974). Theoretical Statistics. London: Chapman & Hall.
-
Daubechies, I. (1992). Ten Lectures on Wavelets. Vol. 61 of CBMS-NSF Regional Conference Series in Applied Mathematics. Philadelphia: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics.
-
Davies, L. (1992). “The Asymptotics of Rousseeuw’s Minimum Volume Ellipsoid Estimator.” Annals of Statistics 20:1828–1843.
-
De Boor, C. (1978). A Practical Guide to Splines. New York: Springer-Verlag.
-
De Jong, P. (1991). “Stable Algorithms for the State Space Model.” Journal of Time Series Analysis 12:143–157.
-
Dennis, J. E., Gay, D. M., and Welsch, R. E. (1981). “An Adaptive Nonlinear Least-Squares Algorithm.” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 7:348–368.
-
Dennis, J. E., and Mei, H. H. W. (1979). “Two New Unconstrained Optimization Algorithms Which Use Function and Gradient Values.” Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications 28:453–482.
-
Devroye, L. (1986). Non-uniform Random Variate Generation. New York: Springer-Verlag. http://luc.devroye.org/rnbookindex.html.
-
Donelson, J., and Hansen, E. (1971). “Cyclic Composite Predictor-Corrector Methods.” SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis 8:137–157.
-
Donoho, D. L., and Johnstone, I. M. (1994). “Ideal Spatial Adaptation via Wavelet Shrinkage.” Biometrika 81:425–455.
-
Donoho, D. L., and Johnstone, I. M. (1995). “Adapting to Unknown Smoothness via Wavelet Shrinkage.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 90:1200–1224.
-
Duchon, J. (1976). “Fonctions-spline et espérances conditionnelles de champs gaussiens.” Annales scientifiques de l’Université de Clermont-Ferrand 2, Série Mathématique 14:19–27.
-
Emerson, P. L. (1968). “Numerical Construction of Orthogonal Polynomials from a General Recurrence Formula.” Biometrics 24:695–701.
-
Eskow, E., and Schnabel, R. B. (1991). “Algorithm 695: Software for a New Modified Cholesky Factorization.” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 17:306–312.
-
Fishman, G. S. (1996). Monte Carlo: Concepts, Algorithms, and Applications. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Fletcher, R. (1987). Practical Methods of Optimization. 2nd ed. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Fletcher, R., and Xu, C. (1987). “Hybrid Methods for Nonlinear Least Squares.” Journal of Numerical Analysis 7:371–389.
-
Forsythe, G. E., Malcom, M. A., and Moler, C. B. (1967). Computer Solution of Linear Algebraic Systems. Chapter 17. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
-
Furnival, G. M., and Wilson, R. W. (1974). “Regression by Leaps and Bounds.” Technometrics 16:499–511.
-
Gaffney, P. W. (1984). “A Performance Evaluation of Some FORTRAN Subroutines for the Solution of Stiff Oscillatory Ordinary Differential Equations.” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 10:58–72.
-
Gay, D. M. (1983). “Subroutines for Unconstrained Minimization.” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 9:503–524.
-
Gentle, J. E. (2003). Random Number Generation and Monte Carlo Methods. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
-
Gentleman, W. M., and Sande, G. (1966). “Fast Fourier Transforms for Fun and Profit.” AFIPS Proceedings of the Fall Joint Computer Conference 19:563–578.
-
George, J. A., and Liu, J. W. (1981). Computer Solutions of Large Sparse Positive Definite Systems. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
-
Geweke, J., and Porter-Hudak, S. (1983). “The Estimation and Application of Long Memory Time Series Models.” Journal of Time Series Analysis 4:221–238.
-
Gill, P. E., Murray, W., Saunders, M. A., and Wright, M. H. (1984). “Procedures for Optimization Problems with a Mixture of Bounds and General Linear Constraints.” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 10:282–298.
-
Golub, G. H. (1969). “Matrix Decompositions and Statistical Calculations.” In Statistical Computation, edited by R. C. Milton, and J. A. Nelder, 365–397. New York: Academic Press.
-
Golub, G. H., and Van Loan, C. F. (1989). Matrix Computations. 2nd ed. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
-
Gonin, R., and Money, A. H. (1989). Nonlinear
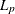 -Norm Estimation. New York: Marcel Dekker.
-Norm Estimation. New York: Marcel Dekker.
-
Goodnight, J. H. (1979). “A Tutorial on the Sweep Operator.” American Statistician 33:149–158.
-
Graybill, F. A. (1969). Introduction to Matrices with Applications in Statistics. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
-
Grizzle, J. E., Starmer, C. F., and Koch, G. G. (1969). “Analysis of Categorical Data by Linear Models.” Biometrics 25:489–504.
-
Hadley, G. (1962). Linear Programming. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
-
Harvey, A. C. (1989). Forecasting, Structural Time Series Models, and the Kalman Filter. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
-
Harville, D. A. (1997). Matrix Algebra from a Statistician’s Perspective. New York: Springer-Verlag.
-
Hocking, R. R. (1985). The Analysis of Linear Models. Monterey, CA: Brooks/Cole.
-
Jenkins, M. A., and Traub, J. F. (1970). “A Three-Stage Algorithm for Real Polynomials Using Quadratic Iteration.” SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis 7:545–566.
-
Jennrich, R. I., and Moore, R. H. (1975). “Maximum Likelihood Estimation by Means of Nonlinear Least Squares.” American Statistical Association, 1975 Proceedings of the Statistical Computing Section 57–65.
-
Johnson, M. E. (1987). Multivariate Statistical Simulation. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Kaiser, H. F., and Caffrey, J. (1965). “Alpha Factor Analysis.” Psychometrika 30:1–14.
-
Kastenbaum, M. A., and Lamphiear, D. E. (1959). “Calculation of Chi-Square to Test the No Three-Factor Interaction Hypothesis.” Biometrics 15:107–122.
-
Kohn, R., and Ansley, C. F. (1982). “A Note on Obtaining the Theoretical Autocovariances of an ARMA Process.” Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation 15:273–283.
-
Korff, F. A., Taback, M. A. M., and Beard, J. H. (1952). “A Coordinated Investigation of a Food Poisoning Outbreak.” Public Health Reports 67:909–913.
-
Kotz, S., Balakrishnan, N., and Johnson, N. L. (2000). Continuous Multivariate Distributions. 2nd ed. New York: Wiley-Interscience.
-
Kotz, S., and Nadarajah, S. (2004). Multivariate t Distributions and Their Applications. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
-
Kruskal, J. B. (1964). “Multidimensional Scaling by Optimizing Goodness of Fit to a Nonmetric Hypothesis.” Psychometrika 29:1–27.
-
Lee, W., and Gentle, J. E. (1986). “The LAV Procedure.” In SUGI Supplemental Library User’s Guide, 257–260. Cary, NC: SAS Institute Inc.
-
Lewart, C. R. (1973). “Algorithm 463: Algorithms SCALE1, SCALE2, and SCALE3 for Determination of Scales on Computer Generated Plots.” Communications of the ACM 16:639–640. http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/362375.362417.
-
Lindström, P., and Wedin, P. A. (1984). “A New Line-Search Algorithm for Nonlinear Least-Squares Problems.” Mathematical Programming 29:268–296.
-
Madsen, K., and Nielsen, H. B. (1993). “A Finite Smoothing Algorithm for Linear
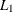 Estimation.” SIAM Journal on Optimization 3:223–235.
Estimation.” SIAM Journal on Optimization 3:223–235.
-
Mallat, S. (1989). “Multiresolution Approximation and Wavelets.” Transactions of the American Mathematical Society 315:69–88.
-
Matsumoto, M., and Nishimura, T. (1998). “Mersenne Twister: A 623-Dimensionally Equidistributed Uniform Pseudo-random Number Generator.” ACM Transactions on Modeling and Computer Simulation 8:3–30.
-
Matsumoto, M., and Nishimura, T. (2002). “Mersenne Twister with Improved Initialization.” Accessed April 10, 2015. http://www.math.sci.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/~m-mat/MT/MT2002/emt19937ar.html.
-
McKean, J. W., and Schrader, R. M. (1987). “Least Absolute Errors Analysis of Variance.” In Statistical Data Analysis Based on
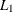 Norm and Related Methods, edited by Y. Dodge, 297–305. Amsterdam: North-Holland.
Norm and Related Methods, edited by Y. Dodge, 297–305. Amsterdam: North-Holland.
-
McLeod, A. I. (1975). “Derivation of the Theoretical Autocovariance Function of Autoregressive–Moving Average Time Series.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series C 24:255–256.
-
Mittnik, S. (1990). “Computation of Theoretical Autocovariance Matrices of Multivariate Autoregressive Moving Average Time Series.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B 52:151–155.
-
Moler, C. B. (2004). Numerical Computing with MATLAB. Natick, MA: MathWorks. http://www.mathworks.com/moler.
-
Moler, C. B. (2011). Experiments with MATLAB. Natick, MA: MathWorks. Available as e-book only. http://www.mathworks.com/moler/exm/chapters.html.
-
Monro, D. M., and Branch, J. L. (1977). “Algorithm AS 117: The Chirp Discrete Fourier Transform of General Length.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series C 26:351–361.
-
Moré, J. J. (1978). “The Levenberg-Marquardt Algorithm: Implementation and Theory.” In Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol. 30, edited by G. A. Watson, 105–116. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
-
Moré, J. J., and Sorensen, D. C. (1983). “Computing a Trust-Region Step.” SIAM Journal on Scientific and Statistical Computing 4:553–572.
-
Nelder, J. A., and Wedderburn, R. W. M. (1972). “Generalized Linear Models.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series A 135:370–384.
-
Nijenhuis, A., and Wilf, H. S. (1978). Combinatorial Algorithms. New York: Academic Press.
-
Nussbaumer, H. J. (1982). Fast Fourier Transform and Convolution Algorithms. 2nd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag.
-
Ogden, R. T. (1997). Essential Wavelets for Statistical Applications and Data Analysis. Boston: Birkhäuser.
-
Osborne, M. R. (1985). Finite Algorithms in Optimization and Data Analysis. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Pizer, S. M. (1975). Numerical Computing and Mathematical Analysis. Chicago: Science Research Associates.
-
Pocock, S. J. (1977). “Group Sequential Methods in the Design and Analysis of Clinical Trials.” Biometrika 64:191–199.
-
Pocock, S. J. (1982). “Interim Analyses for Randomized Clinical Trials: The Group Sequential Approach.” Biometrics 38:153–162.
-
Powell, M. J. D. (1977). “Restart Procedures for the Conjugate Gradient Method.” Mathematical Programming 12:241–254.
-
Powell, M. J. D. (1978). “A Fast Algorithm for Nonlinearly Constrained Optimization Calculations.” In Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol. 630, edited by G. A. Watson, 144–175. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
-
Powell, M. J. D. (1982). VMCWD: A Fortran Subroutine for Constrained Optimization. Technical Report DAMTP 1982/NA4, Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge.
-
Powell, M. J. D. (1992). A Direct Search Optimization Method That Models the Objective and Constraint Functions by Linear Interpolation. Technical Report DAMTP 1992/NA5, Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge.
-
Ralston, A., and Rabinowitz, P. (1978). A First Course in Numerical Analysis. New York: McGraw-Hill.
-
Rao, C. R., and Mitra, S. K. (1971). Generalized Inverse of Matrices and Its Applications. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Reinsch, C. H. (1967). “Smoothing by Spline Functions.” Numerische Mathematik 10:177–183.
-
Reinsel, G. C. (1997). Elements of Multivariate Time Series Analysis. 2nd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag.
-
Rice, S. O. (1973). “Efficient Evaluation of Integrals of Analytic Functions by the Trapezoidal Rule.” Bell System Technical Journal 52:707–722.
-
Rousseeuw, P. J. (1984). “Least Median of Squares Regression.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 79:871–880.
-
Rousseeuw, P. J. (1985). “Multivariate Estimation with High Breakdown Point.” In Mathematical Statistics and Applications, edited by W. Grossmann, G. Pflug, I. Vincze, and W. Wertz, 283–297. Dordrecht, Netherlands: D. Reidel Publishing.
-
Rousseeuw, P. J., and Croux, C. (1993). “Alternatives to the Median Absolute Deviation.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 88:1273–1283.
-
Rousseeuw, P. J., and Hubert, M. (1996). “Recent Development in PROGRESS.” Computational Statistics and Data Analysis 21:67–85.
-
Rousseeuw, P. J., and Hubert, M. (1997). “Recent Developments in PROGRESS.”
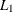 -Statistical Procedures and Related Topics .
-Statistical Procedures and Related Topics .
-
Rousseeuw, P. J., and Leroy, A. M. (1987). Robust Regression and Outlier Detection. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
-
Rousseeuw, P. J., and Van Driessen, K. (1998). Computing LTS Regression for Large Data Sets. Technical report, University of Antwerp.
-
Rousseeuw, P. J., and Van Driessen, K. (1999). “A Fast Algorithm for the Minimum Covariance Determinant Estimator.” Technometrics 41:212–223.
-
Rousseeuw, P. J., and Van Zomeren, B. C. (1990). “Unmasking Multivariate Outliers and Leverage Points.” Journal of the American Statistical Association 85:633–639.
-
Schatzoff, M., Tsao, R., and Fienberg, S. (1968). “Efficient Calculation of All Possible Regressions.” Technometrics 10:769–779.
-
Shampine, L. (1978). “Stability Properties of Adams Codes.” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 4:323–329.
-
Sikorsky, K. (1982). “Optimal Quadrature Algorithms in
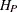 Spaces.” Numerische Mathematik 39:405–410.
Spaces.” Numerische Mathematik 39:405–410.
-
Sikorsky, K., and Stenger, F. (1984). “Optimal Quadratures in
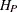 Spaces.” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 3:140–151.
Spaces.” ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software 3:140–151.
-
Singleton, R. C. (1969). “An Algorithm for Computing the Mixed Radix Fast Fourier Transform.” IEEE Transactions on Audio and Electroacoustics 17:93–103.
-
Sowell, F. (1992). “Maximum Likelihood Estimation of Stationary Univariate Fractionally Integrated Time Series Models.” Journal of Econometrics 53:165–188.
-
Squire, W. (1987). “Comparison of Gauss-Hermite and Midpoint Quadrature with Application to the Voigt Function.” In Numerical Integration: Recent Developments, edited by P. Keast, and G. Fairweather, 111–112. Dordrecht, Netherlands: D. Reidel Publishing.
-
Stenger, F. (1973a). “Integration Formulas Based on the Trapezoidal Formula.” Journal of the Institute of Mathematics and Its Applications 12:103–114.
-
Stenger, F. (1973b). “Remarks on Integration Formulas Based on the Trapezoidal Formula.” Journal of the Institute of Mathematics and Its Applications 19:145–147.
-
Stenger, F. (1978). “Optimal Convergence of Minimum Norm Approximations in
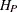 .” Numerische Mathematik 29:345–362.
.” Numerische Mathematik 29:345–362.
-
Stoer, J., and Bulirsch, R. (1980). Introduction to Numerical Analysis. New York: Springer-Verlag.
-
Thisted, R. A. (1988). Elements of Statistical Computing: Numerical Computation. London: Chapman & Hall.
-
Trotter, H. F. (1962). “Algorithm 115: PERM.” Communications of the ACM 5:434–435.
-
Wahba, G. (1990). Spline Models for Observational Data. Philadelphia: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics.
-
Wang, S. K., and Tsiatis, A. A. (1987). “Approximately Optimal One Parameter Boundaries for Group Sequential Trials.” Biometrics 43:193–199.
-
Wilkinson, J. H., and Reinsch, C. (1971). Handbook for Automatic Computation: Linear Algebra. Vol. 2. New York: Springer-Verlag.
-
Woodfield, T. J. (1988). “Simulating Stationary Gaussian ARMA Time Series.” In Computing Science and Statistics: Proceedings of the Twentieth Symposium on the Interface (Fairfax, VA), edited by E. J. Wegman, D. T. Gantz, and J. J. Miller, 612–617. Alexandria, VA: American Statistical Association.
-
Young, F. W. (1981). “Quantitative Analysis of Qualitative Data.” Psychometrika 46:357–388.