Language Reference
LAG Function
LAG (x <, lags> );
The LAG function computes one or more lagged (shifted) values for time series data. The arguments are as follows:
- x
-
specifies an
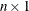 numerical matrix of time series data.
numerical matrix of time series data.
- lags
-
specifies integer lags. The lags argument can be an integer matrix with d elements. If so, the LAG function returns an
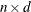 matrix where the ith column represents the ith lag applied to the time series. If the lags argument is not specified, a value of 1 is used.
matrix where the ith column represents the ith lag applied to the time series. If the lags argument is not specified, a value of 1 is used.
The values of the lags argument are usually positive integers. A positive lag shifts the time series data backwards in time. A lag of 0 represents the original time series. A negative value for the lags argument shifts the time series data forward in time; this is sometimes called a lead effect. The LAG function is related to the DIF function .
For example, the following statements compute several lags:
x = {1,3,4,7,9};
lag = lag(x, {0 1 3});
print lag;