Defining a Matrix
A matrix is the fundamental structure in the SAS/IML language. A matrix is a two-dimensional array of numeric or character values. Matrices are useful for working with data and have the following properties:
Matrices can be either numeric or character. Elements of a numeric matrix are double-precision values. Elements of a character matrix are character strings of equal length.
The name of a matrix must be a valid SAS name.
Matrices have dimensions defined by the number of rows and columns.
Matrices can contain elements that have missing values (see the section Missing Values).
The dimensions of a matrix are defined by the number of rows and columns. An 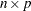 matrix has
matrix has 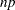 elements arranged in
elements arranged in  rows and
rows and 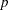 columns. The following nomenclature is standard in this book:
columns. The following nomenclature is standard in this book:
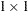 matrices are called scalars.
matrices are called scalars. 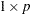 matrices are called row vectors.
matrices are called row vectors. 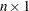 matrices are called column vectors.
matrices are called column vectors. The type of a matrix is "numeric" if its elements are numbers; the type is "character" if its elements are character strings. A matrix that has not been assigned values has an "undefined" type.