You can use the Output Variables tab to add analysis variables to the data table. (See Figure 21.17.) If you request a plot that uses one of the output variables, then that variable is automatically created even if you did not explicitly select the variable on the Output Variables tab.
The following list describes each output variable and indicates how the output variable is named. ![]() represents the name of the response variable.
represents the name of the response variable.
- Predicted values
-
adds predicted values. The variable is named
RegP_.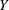
- Confidence limits for means
-
adds 95% confidence limits for the expected value (mean). The variables are named
RegLclm_and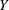
RegUclm_.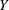
- Prediction limits for individuals
-
adds 95% confidence limits for an individual prediction. The variables are named
RegLcli_and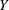
RegUcli_.
- Raw residuals
-
adds residuals, which are calculated as observed values minus predicted values. The variable is named
RegR_.
- Internally studentized residuals
-
adds internally studentized residuals, which are the residuals divided by their standard errors. (These correspond to the STUDENT= option in the OUTPUT statement.) The variable is named
RegIntR_.
- Externally studentized residuals
-
adds externally studentized residuals, which are studentized residuals with the current observation deleted. (These correspond to the RSTUDENT= option in the OUTPUT statement.) The variable is named
RegExtR_.
- Cook’s D
-
adds Cook’s
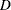 influence statistic. The variable is named
influence statistic. The variable is named RegCooksD_.
- Leverage (H)
-
adds the leverage statistic. The variable is named
RegH_.
- PRESS residuals
-
adds the PRESS residuals. This is the
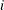 th residual divided by
th residual divided by 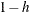 , where
, where 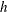 is the leverage and where the model has been refit without the
is the leverage and where the model has been refit without the 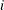 th observation. The variable is named
th observation. The variable is named RegPRESS_.
- COVRATIO (influence on covariance of coefficients)
-
adds the covariance ratio. This is the
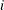 th residual divided by
th residual divided by 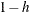 , where
, where 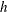 is the leverage and where the model has been refit without the
is the leverage and where the model has been refit without the 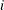 th observation. The variable is named
th observation. The variable is named RegCovRatio_.
- DFFITS (influence on predicted values)
-
adds the standard influence of observation on the predicted value. The variable is named
RegDFFITS_.
- DFBETAS (influence on coefficients)
-
adds
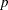 variables, where
variables, where 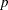 is the number of parameters in the model. The variables are scaled measures of the change in each parameter estimate and
are calculated by deleting the
is the number of parameters in the model. The variables are scaled measures of the change in each parameter estimate and
are calculated by deleting the 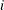 th observation. Large values of DFBETAS indicate observations that are influential in estimating a given parameter. Belsley,
Kuh, and Welsch (1980) recommend
th observation. Large values of DFBETAS indicate observations that are influential in estimating a given parameter. Belsley,
Kuh, and Welsch (1980) recommend 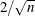 as a size-adjusted cutoff. The variables are named
as a size-adjusted cutoff. The variables are named DFB_, where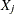
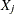 is the name of the
is the name of the  th regressor (including the intercept).
th regressor (including the intercept).
