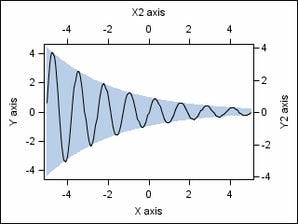
Axes
The GTL
uses various criteria to determine the displayed axis features for
a graph. Generally, axis features are based on the layout type, the
order of plot statements in the layout and the options specified on
those statements, the use of “primary” and “secondary”
axes on the plots (when secondary axes are supported), the plot type,
the column(s) of data that contribute to defining the axis range,
and the data formats for the contributing data columns.
Depending
on the layout type, 2-D plots can have up to four independent axes
that can be displayed: X, Y, X2, and Y2. The X and Y axes are considered
the primary axes, and the X2 and Y2 axes are considered the secondary
axes. By default, the X2 and Y2 axes are not displayed. When requested,
the secondary axes can be displayed as copies of the primary axes,
or data can be mapped separately to them. The following figure identifies
the X, Y, X2, and Y2 axes.
For more
information about axis features in GTL, see Axis Features in Layouts.