SAS/GRAPH
A group of SAS procedure statements is
called a PROC step. The PROC step consists of all the statements,
variables, and options that are contained within the (beginning) PROC 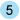 and (ending) RUN
and (ending) RUN 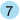 statements of a procedure. These statements can
identify and analyze the data in SAS data sets. They can generate
the graphics output and control the appearance of the output. Statements
can define variables and perform other operations on your data. You
can also specify global statements and options within the PROC step
to customize the appearance of your graph. However, it is often more
efficient to specify global statements before the PROC step.
statements of a procedure. These statements can
identify and analyze the data in SAS data sets. They can generate
the graphics output and control the appearance of the output. Statements
can define variables and perform other operations on your data. You
can also specify global statements and options within the PROC step
to customize the appearance of your graph. However, it is often more
efficient to specify global statements before the PROC step.
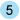 and (ending) RUN
and (ending) RUN 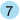 statements of a procedure. These statements can
identify and analyze the data in SAS data sets. They can generate
the graphics output and control the appearance of the output. Statements
can define variables and perform other operations on your data. You
can also specify global statements and options within the PROC step
to customize the appearance of your graph. However, it is often more
efficient to specify global statements before the PROC step.
statements of a procedure. These statements can
identify and analyze the data in SAS data sets. They can generate
the graphics output and control the appearance of the output. Statements
can define variables and perform other operations on your data. You
can also specify global statements and options within the PROC step
to customize the appearance of your graph. However, it is often more
efficient to specify global statements before the PROC step.
Subordinate Statement
Subordinate statements  are statements used within the procedure that perform
the work of the procedure. Subordinate statements that generate graphs
are called action statements. At least
one action statement is required for a procedure to produce a graph.
Examples of action statements are the HBAR statement in the GCHART
procedure and the BUBBLE statement in the GPLOT procedure.
are statements used within the procedure that perform
the work of the procedure. Subordinate statements that generate graphs
are called action statements. At least
one action statement is required for a procedure to produce a graph.
Examples of action statements are the HBAR statement in the GCHART
procedure and the BUBBLE statement in the GPLOT procedure.
 are statements used within the procedure that perform
the work of the procedure. Subordinate statements that generate graphs
are called action statements. At least
one action statement is required for a procedure to produce a graph.
Examples of action statements are the HBAR statement in the GCHART
procedure and the BUBBLE statement in the GPLOT procedure.
are statements used within the procedure that perform
the work of the procedure. Subordinate statements that generate graphs
are called action statements. At least
one action statement is required for a procedure to produce a graph.
Examples of action statements are the HBAR statement in the GCHART
procedure and the BUBBLE statement in the GPLOT procedure.
Other Statements and Options
There are
many options  that you can specify within the PROC step to control
your graphics output. PROC step options always follow the forward
slash (/) following the action statement of the procedure. These options
might control such things as axis characteristics, midpoint values,
statistics, catalog entry descriptions, or appearance elements of
your graph. Take, for example, the SUBGROUP= option in the BLOCK statement
of the GCHART procedure. The option tells the procedure to divide
the graph's bars into segments according to the values of the SUBGROUP=
variable. The HAXIS option
in the PLOT statement of the GPLOT procedure, as shown in Typical SAS/GRAPH Program, specifies
where to draw the major tick mark values for the horizontal axis.
that you can specify within the PROC step to control
your graphics output. PROC step options always follow the forward
slash (/) following the action statement of the procedure. These options
might control such things as axis characteristics, midpoint values,
statistics, catalog entry descriptions, or appearance elements of
your graph. Take, for example, the SUBGROUP= option in the BLOCK statement
of the GCHART procedure. The option tells the procedure to divide
the graph's bars into segments according to the values of the SUBGROUP=
variable. The HAXIS option
in the PLOT statement of the GPLOT procedure, as shown in Typical SAS/GRAPH Program, specifies
where to draw the major tick mark values for the horizontal axis.
 that you can specify within the PROC step to control
your graphics output. PROC step options always follow the forward
slash (/) following the action statement of the procedure. These options
might control such things as axis characteristics, midpoint values,
statistics, catalog entry descriptions, or appearance elements of
your graph. Take, for example, the SUBGROUP= option in the BLOCK statement
of the GCHART procedure. The option tells the procedure to divide
the graph's bars into segments according to the values of the SUBGROUP=
variable. The HAXIS option
in the PLOT statement of the GPLOT procedure, as shown in Typical SAS/GRAPH Program, specifies
where to draw the major tick mark values for the horizontal axis.
that you can specify within the PROC step to control
your graphics output. PROC step options always follow the forward
slash (/) following the action statement of the procedure. These options
might control such things as axis characteristics, midpoint values,
statistics, catalog entry descriptions, or appearance elements of
your graph. Take, for example, the SUBGROUP= option in the BLOCK statement
of the GCHART procedure. The option tells the procedure to divide
the graph's bars into segments according to the values of the SUBGROUP=
variable. The HAXIS option
in the PLOT statement of the GPLOT procedure, as shown in Typical SAS/GRAPH Program, specifies
where to draw the major tick mark values for the horizontal axis.