| The ALLELE Procedure |
Overview: ALLELE Procedure
The ALLELE procedure performs preliminary analyses on genetic marker data. These analyses serve to characterize the markers themselves or the population from which they were sampled, and can also serve as the basis for joint analyses on markers and traits. A genetic marker is any heritable unit that obeys the laws of transmission genetics, and the analyses presented here assume the marker genotypes are determined without error. With an underlying assumption of random sampling, the analyses rest on the multinomial distribution of marker alleles, and many standard statistical techniques can be invoked with little modification. The ALLELE procedure uses the notation and concepts described by Weir (1996); this is the reference for all equations and methods not otherwise cited.
Data are usually collected at the genotypic level, but interest is likely to be centered on the constituent alleles, so the first step is to construct tables of allele and genotype frequencies. When alleles are independent within individuals—that is, when there is Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE)—analyses can be conducted at the allelic level. For this reason the ALLELE procedure allows for Hardy-Weinberg testing, although testing is also recommended as a means for detecting possible errors in data.
PROC ALLELE calculates the PIC, heterozygosity, and allelic diversity measures that serve to give an indication of marker informativeness. Such measures can be useful in determining which markers to use for further linkage or association testing with a trait. High values of these measures are a sign of marker informativeness, which is a desirable property in linkage and association tests.
Associations between markers might also be of interest. PROC ALLELE provides tests and various statistics for the association, also called the linkage disequilibrium, between each pair of markers. These statistics can be formed either by using haplotypes that are given in the data, by estimating the haplotype frequencies, or by using only genotypic information.
Population structure can also be analyzed using the 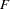 statistics that are reported by PROC ALLELE to describe functions of the various covariance components related to the population group effects.
statistics that are reported by PROC ALLELE to describe functions of the various covariance components related to the population group effects.
Copyright © 2008 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.