Exporting an XML Document for Use by Oracle
This example exports an XML document from a SAS data
set for use by Oracle. By specifying the ORACLE markup type, the XML
engine generates tags that are specific to Oracle standards.
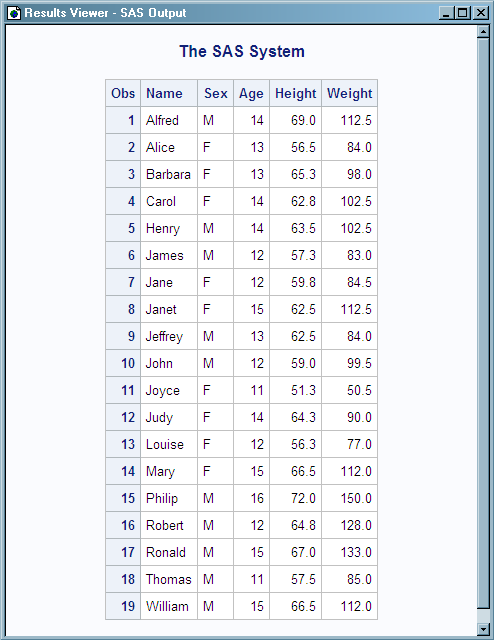
libname myfiles 'SAS-library'; 1 libname trans xml 'XML-document' xmltype=oracle; 2 data trans.class; 3 set myfiles.class; run;
| 1 | The first LIBNAME statement assigns the libref MYFILES to the physical location of the SAS library that stores the SAS data set CLASS. The V9 engine is the default. |
| 2 | The second LIBNAME statement assigns the libref TRANS to the physical location of the file (complete pathname, filename, and file extension) that will store the exported XML document and specifies the XML engine. The engine option XMLTYPE=ORACLE produces tags that are equivalent to the Oracle 8i XML implementation. |
| 3 | The DATA step reads the SAS data set MYFILES.CLASS and writes its content in ORACLE XML markup to the specified XML document. |
XML Document Exported from MYFILES.CLASS to Be Used by Oracle
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="windows-1252" ?> <ROWSET> <ROW> <Name> Alfred </Name> <Gender> M </Gender> <Age> 14 </Age> <Height> 69 </Height> <Weight> 112.5 </Weight> </ROW> <ROW> <Name> Alice </Name> <Gender> F </Gender> <Age> 13 </Age> <Height> 56.5 </Height> <Weight> 84 </Weight> </ROW> . . . <ROW> <Name> William </Name> <Gender> M </Gender> <Age> 15 </Age> <Height> 66.5 </Height> <Weight> 112 </Weight> </ROW> </ROWSET>