Compressing SPD Engine Data Sets
When COMPRESS=YES | BINARY | CHAR, the SPD Engine compresses, by blocks, the data component file as it is created. The SPD Engine does
not support user-specified compression. In addition, if you are copying a default
Base SAS engine data set that is both compressed and encrypted, the encryption is
retained, but the compression is dropped.
Once a compressed data set is created, you cannot change its block size. The compressed blocks are stored linearly, with no spaces between the blocks.
The following figure illustrates how the blocks are stored on the disk:
Compressed Blocks on the Disk
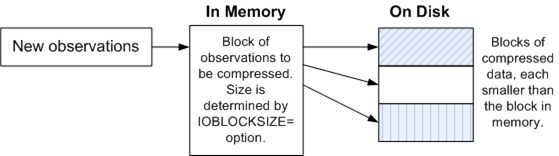
If updates to the data set after compression require more space than what is available
in a block, SPD Engine creates a new block fragment to hold the overflow. If further
updates again cause
overflows, new block fragments are created, forming a chain. The following figure
illustrates how the updates create a chain of blocks on the disk:
Compressed Blocks with Overflow
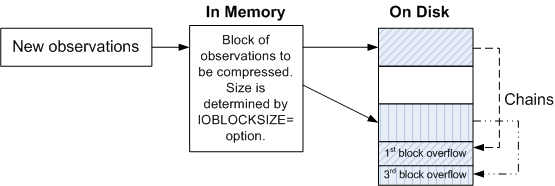
Performance is affected if the chains get too long. To remove the chains and resize
the block, you must copy the data set to a new data set. Specify IOBLOCKSIZE= to the block size appropriate for the output data set.
When the data set is
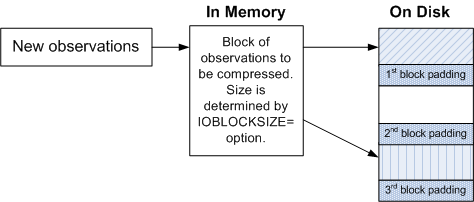
expected to be updated frequently, it is recommended that you use
PADCOMPRESS=. SPD Engine creates a padded space for each block, instead of creating new block fragments.
The following figure illustrates how each
block has padded space for updates:
Compressed Padded Blocks
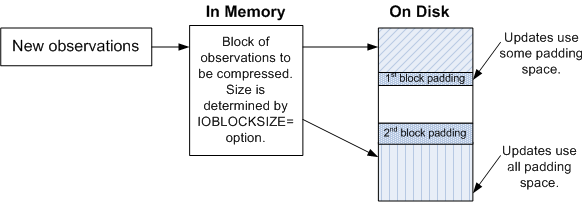
If updates to the data set after compression require more space than what is available
in a block, SPD Engine uses the padded space for each block. New block fragments are
not created. The following
figure illustrates how the updates decrease the padded space:
Compressed Padded Blocks with Updates
The CONTENTS procedure
prints information about the compression. The following example explains
the compressed info fields in the CONTENTS procedure output:
CONTENTS Procedure Compressed Info Output
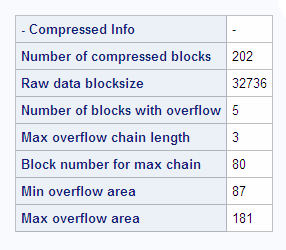
Number of compressed blocks
number of compressed
blocks that are required to store data.
Raw data blocksize
compressed block size in bytes calculated from the size specified in the IOBLOCKSIZE=
data set option.
Number of blocks with overflow
number of compressed blocks that needed more space. When data is updated and the compressed
new block is larger than the compressed old block, an overflow block fragment is created.
Max overflow chain length
largest number of overflows for a single block. For example, the maximum overflow
chain length would be 2 if a compressed block
was updated and became larger, and then updated again to a larger size.
Block number for max chain
number of the block containing the largest number of overflow blocks.
Min overflow area
minimum amount of disk
space that an overflow requires.
Max overflow area
maximum amount of disk
space that an overflow requires.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All Rights Reserved.