What Is Credit Scoring for SAS Enterprise Miner?
Credit
scoring is the set of decision models and their underlying
techniques that aid lenders in the granting of consumer credit. These
techniques describe who should get credit, how much credit they should
receive, and which operational strategies will enhance the profitability
of the borrowers to the lenders (Thomas, Edelman, and Crook 2002).
Credit Scoring, as
defined by SAS, includes the following:
Although credit scoring
is not as glamorous as pricing exotic financial derivatives, it is
one of the most successful applications of statistical and operations
research techniques in finance and banking. Without an accurate and
automated risk assessment tool, the phenomenal growth of consumer
credit would not have been possible over the past 40 years (Thomas,
Edelman, and Crook 2002).
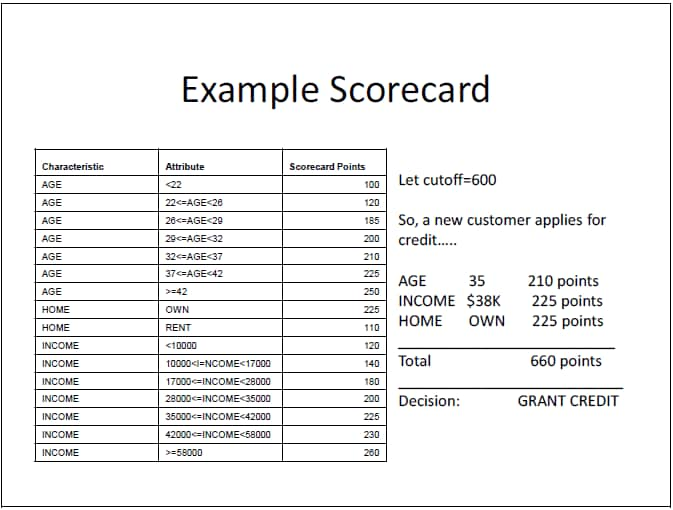
In its simplest form,
a scorecard is built from a number of characteristics (that is, input
or predictor variables). Each characteristic includes a number of
attributes. For example, age is a characteristic, and “25-33”
is an attribute. Each attribute is associated with a number of scorecard
points. These scorecard points are statistically assigned to differentiate
risk, based on the predictive power of the characteristic variables,
correlation between the variables, and business considerations.
For example, using the
Example Scorecard in Figure 1.1, an applicant who is 35, makes $38,000,
and is a homeowner would be accepted for credit by this financial
institution’s scorecard. The total score of an applicant is
the sum of the scores for each attribute that is present in the scorecard.
Lower scores imply a higher risk of default, and higher scores imply
a lower risk of default.
Credit Scoring for SAS
Enterprise Miner contains the following nodes, which are added to
your SAS Enterprise Miner toolbar to support scorecard development:
-
Scorecard — uses the grouped variables as inputs in a logistic regression model and usually follows the Interactive Grouping node. In addition, it scales the regression parameters to compute score points and the resulting scorecard. Finally, the Scorecard node performs score and characteristic (variable) analysis that helps in understanding the scorecard, and aids in crafting a score-based strategy.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.