Indicator Data Rules
Here are several
rules to help you to create quicker and more efficient indicator data:
-
Plan the indicator data by considering the indicator display types that will be used with the indicator data and the required appearance of the desired end result.For example, KPIs appear best with indicator data that produces summarized data with a limited number of data rows. Indicator data with significant amounts of data, when used to drive a KPI indicator display, causes the SAS BI Dashboard to try to produce one KPI graphic representation for each row of data in the indicator data. Other indicator display types, such as the bar chart, automatically summarize the data. In this case, it might be appropriate to use indicator data that produces a larger number of data rows.
-
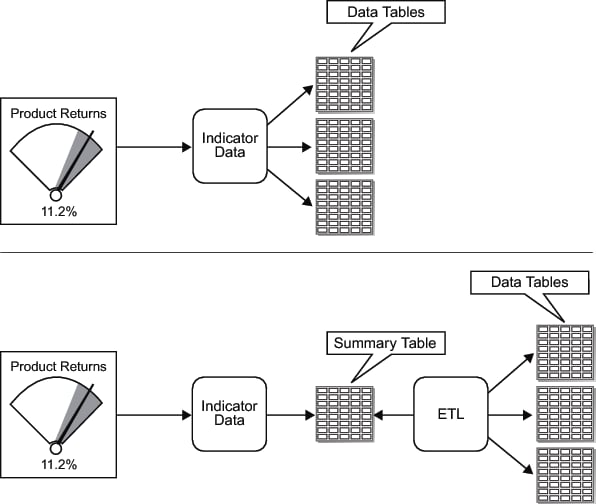
If the source data has too many rows, summarize the data.Summarize data at the indicator data or data-model level. Do not rely on the indicator display to perform the summary.For an SQL query, you can summarize data using aggregation functions such as AVG() and the distinct keyword.Another summarization strategy is to summarize the data into a summary table. The summary table is then used as the basis for the SQL query or as the base table for the information map. The first illustration that follows shows the SAS BI Dashboard indicator data using a query that combines data from multiple tables. The second illustration shows the same two tables being summarized by an ETL program. The SAS BI Dashboard indicator data then uses this summarized table.
-
To display multiple gauges or a graph in an indicator, each numeric value should be associated with a descriptive name.After you define indicator data, you select the data fields to include in the indicator display. For every numeric data field displayed in the indicator, you can select a data field from the Category Label drop-down list to associate with the numeric value. This associated data field is displayed with the gauge or the category value in a graph.