Configure Multiple Clients to Read from a Single Queue
The WebSphere MQ interfaces
and the message queue polling feature of the object spawner can be
used to distribute the processing of messages on a message queue across
one or more machines. The result is enhanced performance, load balancing,
and hardware redundancy.
Messages can be retrieved
only from local queues. In order to enable multiple machines to process
messages on a single queue, you must have a full WebSphere MQ (server)
installation on the machine that will act as the server. The WebSphere
MQ Clients use the queue manager on the server as their queue manager,
so any local queues that are defined on that queue manager are also
local to the client installations. The WebSphere MQ Clients can connect
to a WebSphere MQ server on any supported platform. Message queuing
applications on the machine where the queue manager is installed can
access the queues directly. Message queuing applications do not need
to be configured as clients.
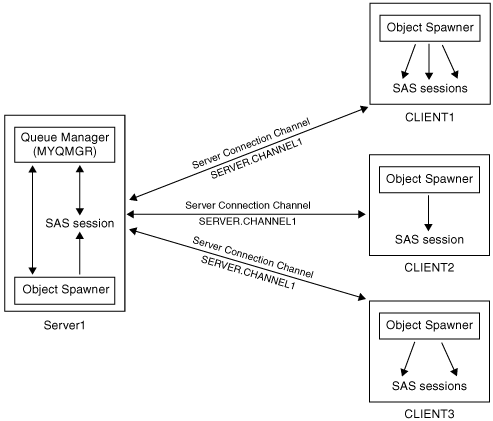
The following diagram
illustrates a sample configuration. The queue manager (MYQMGR) is
running on Server1 and is managing the queue for each of the WebSphere
MQ Clients (CLIENT1, CLIENT2, and CLIENT3). All three clients are
communicating with the queue manager through the same server connection
channel (SERVER.CHANNEL1). The object spawners on each of the clients
can start one or more SAS sessions as needed in order to receive messages
from the queue. SAS sessions can also be started by the object spawner
and run on the server. A SAS session running on the server does not
need to run as a WebSphere MQ Client application; it behaves as a
WebSphere MQ server application.
-
On each client, install and configure the WebSphere MQ Client. Use the MQSERVER environment variable to define the client connection to the server. The following code shows examples of how to do this in Windows and UNIX operating environments.
-
set MQSERVER=ChannelName/TransportType/ConnectionName
set MQSERVER=SERVER.CHANNEL1/TCP/server_address(port)
where server_address is the TCP/IP host name of the server and port is the number of the TCP/IP port on which the server is listening. The default port number is 1414. Here is an example:set MQSERVER=SERVER.CHANNEL1/TCP/10.12.0.0(1414)
-
-
The queue and queue manager values are required in SAS applications that use the WebSphere MQ functional interface. In the previous examples, the queue manager is named MYQMGR, and the queue is named LOCAL. These values are used as follows in the SAS DATA step application:
hConn=0; Name="MYQMGR"; compCode=0; reason=0; CALL MQCONN(Name, hConn, compCode, reason); action = "GEN"; parms="OBJECTNAME"; objname="LOCAL"; call mqod(hod, action, rc, parms, objname); options="INPUT_SHARED"; call mqopen(hconn, hod, options, hobj, compCode, reason);
If a SAS application is running as a WebSphere MQ Client, then you must include the following line of code before making any calls that use the WebSphere MQ Functional Interface. This line should go at the beginning of the application before the DATA step:%let MQMODEL=CLIENT; data _null_; ... run;