Implementing Custom Menus
Introduction
You can create custom menus for your SAS/AF applications using the Base SAS software PMENU procedure.
To add a menu to your
application:
-
Create a PMENU catalog entry using PROC PMENU.
-
In the SAS/AF build environment, use the Properties window to set the appropriate frame's
pmenuEntryattribute to the PMENU catalog entry that you want to display. -
Set the frame's
forcePmenuOnattribute toYesand the frame'sbannerTypeattribute toNone.
For additional information
about PMENU entries, see the SAS/AF
online Help.
Using the PMENU Procedure to Create Menus
To create the structures and commands associated with your menu, you submit a source
program that contains PMENU procedure statements. Because the source statements that
are used to create a PMENU entry are not accessible in the PMENU catalog entry, you
should save the statements in your development catalog as a SOURCE entry.
Consider the following
example:
proc pmenu catalog=sasuser.corprpts;
menu main;
item 'File' menu=menuFile mnemonic='F';
item 'View' menu=menuView mnemonic='V';
item 'Help' menu=menuHelp mnemonic='H';
menu menuFile;
item 'Open Report' selection=fileOpen mnemonic='O';
item 'Save Report' selection=fileSave mnemonic='S';
separator;
item 'End';
selection fileOpen 'openrpt';
selection fileSave 'saverpt';
menu menuView;
item 'View Table' selection=viewTbl mnemonic='T';
item 'Options' selection=viewOpts mnemonic='p';
selection viewTbl 'afa c=mylib.mycat.view.frame';
selection viewOpts 'afa c=mylib.mycat.options.frame';
menu menuHelp;
item 'Contents' selection=helpCont mnemonic='C';
item 'About...' selection=helpAbt mnemonic='A';
selection helpCont 'wbrowse "http://myintranet.com/help.htm"';
selection helpAbt 'afa c=mylib.mycat.about.frame';
run;
quit;In this example,
-
The menu is stored in the catalog named in the PROC PMENU statement.
-
The first menu statement names the PMENU catalog entry that will contain the menu, which in this example is
sasuser.corprpts.main.pmenu. -
Each ITEM statement specifies an item in the menu bar. The value of MENU= corresponds to a subsequent MENU statement.
-
Each MENU= option is defined by a MENU statement, where each subsequent ITEM statement specifies the selections that are available under the named menu in the menu bar.
-
A separator line can be added to menus by using the SEPARATOR statement.
-
ITEM statements with no SELECTION= option indicate that the menu command is equivalent to the value of the ITEM. For example,
item 'End'in the menuFile menu is theEndcommand. -
Each SELECTION= option points to a corresponding SELECTION statement to define the command that is issued by the menu.Note: To issue multiple commands, separate them with semicolons.
-
Commands in a SELECTION statement that do not correspond to a valid SAS command must be implemented and trapped in the frame's SCL program.
The completed menu appears
as follows:
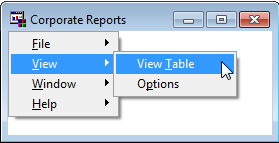
In the PMENU example,
the menuFile menu contains two SELECTION statements that issue the
custom commands
openrpt and saverpt. Your frame SCL program can process commands that are not valid SAS commands if
-
the command name is not a valid AF window command or SAS global command
-
your frame SCL includes a CONTROL ALWAYS or CONTROL ENTER option
-
the MAIN section in your frame SCL performs the processing
For example, the SCL program for the frame associated with MAIN.PMENU could include
the following code:
dcl char(8) command;
INIT:
control always;
return;
MAIN:
command=lowcase(word(1));
if command='openrpt' then do;
/* ...SCL to open reports... */
call nextcmd();
end;
else if command='saverpt' then do;
/* ...SCL to save reports... */
call nextcmd();
end;
return;For complete information
on the PMENU procedure, refer to the SAS Procedures Guide.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Last updated: May 27, 2017