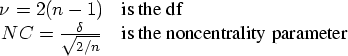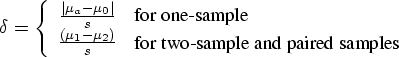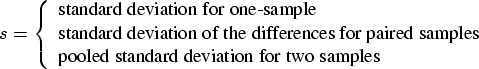| Sample Size and Power Calculations |
Hypothesis Tests
The power for the one-sample t-test, the paired t-test, and the two-sample t-test is computed in the usual fashion. That is, power is the probability of correctly rejecting the null hypothesis when the alternative is true. The sample size is the number per group; these calculations assume equally sized groups. To compute the power of a t-test, you make use of the noncentral t distribution. The formula (O'Brien and Lohr 1984) is given by
for a one-sided alternative hypothesis and
for a two-sided alternative hypothesis where t is distributed as noncentral ![]() .
.
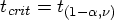 is the (
is the (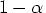 ) quantile of the t distribution with
) quantile of the t distribution with 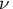 df
df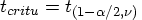 is the (1-
is the (1-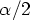 ) quantile of the t distribution with
) quantile of the t distribution with 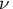 df
df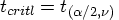 is the (
is the (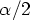 ) quantile of the t distribution with
) quantile of the t distribution with 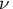 df
df
For one sample and paired samples,
For two samples,
Note that n equals the sample size (number per group).
The other parameters are
Copyright © 2007 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.