| Plackett-Burman Designs |
Automatic Selection Methods
By default, ADX uses the ANOVA automatic selection method for this design because three degrees of freedom are available for estimating error. You can choose a different method for selecting active effects with the Identify menu. See the section "Analyzing Saturated Designs" for more details about which automatic selection methods are used by default.
Lenth's Method and the Lenth Plot
To select effects with Lenth's method and to display a Lenth plot, follow these steps:- Select Identify
 Select effects
Select effects  Automatic
Automatic  Lenth.
Lenth.
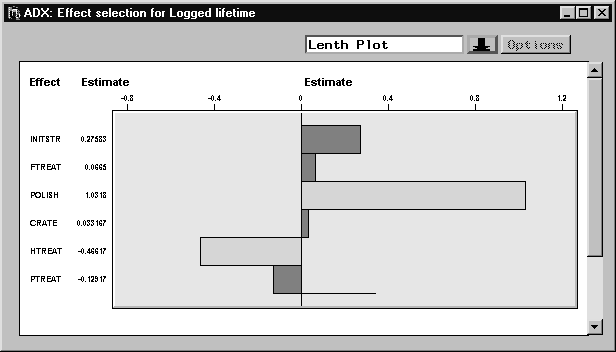
- Change the display to the Lenth plot. The Lenth plot shows the significant effects highlighted at the
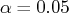 level. You always have the option of manually selecting or removing factors based on the size and direction of the estimate.
level. You always have the option of manually selecting or removing factors based on the size and direction of the estimate.
|
Bayesian Effect Selection
ADX also provides the Bayesian effect selection method described in Box and Meyer (1986), which is a useful supplement to the ANOVA and Lenth methods. Note that the Bayesian and Lenth methods apply to saturated designs, whereas ANOVA does not.
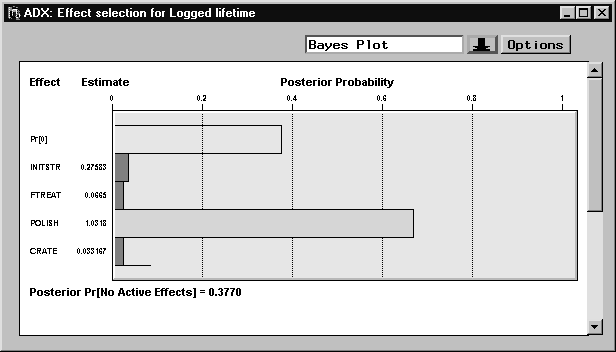
To use the Bayesian method, click the down arrow in the Effect Selection for Logged lifetime window and select Bayes plot. A default Bayes plot appears. The default assumes a 0.2 prior probability for an effect to be active, and the bars display the posterior probability that each effect is still active. Bayesian analysis selects the same factors previously identified as significant.
|
The bar labeled Pr[0] indicates the posterior probability that no effects are active given the prior distribution.
Box and Meyer (1986) recommend that effect selection be performed over a range of priors before a final model is fit. To change the prior probability distribution, do the following:
- Click Options while the Bayes plot is displayed.
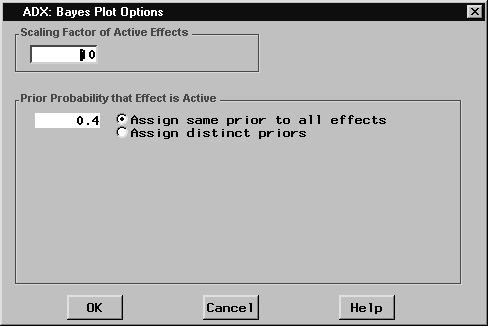
- A dialog box will appear with two groups of options. The bottom group affects the prior distribution.
- If you want to set the prior distribution uniformly for all effects, select Assign same prior to all effects and type the prior probability that each individual effect is active. For example, type 0.4 in the text field.
- Click OK to apply the changes to the plot.
If, based on prior experience, you feel that some effects are more likely to be active, you can select Assign distinct priors in the Bayes Plot Options dialog box and assign each prior separately.
You can specify the Bayesian method as the default selection method by selecting Identify ![]() Select effects
Select effects ![]() Automatic
Automatic ![]() Bayes cutoff. By default, an effect will be selected as active if its posterior probability is 0.5 or greater. You can change the cutoff, or click OK to apply the effect selection method.
Bayes cutoff. By default, an effect will be selected as active if its posterior probability is 0.5 or greater. You can change the cutoff, or click OK to apply the effect selection method.
Copyright © 2008 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.